Use of a human-like low-grade bacteremia model of experimental endocarditis to study the role of Staphylococcus aureus adhesins and platelet aggregation in early endocarditis
- PMID: 23250949
- PMCID: PMC3584864
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01030-12
Use of a human-like low-grade bacteremia model of experimental endocarditis to study the role of Staphylococcus aureus adhesins and platelet aggregation in early endocarditis
Abstract
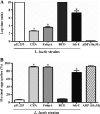
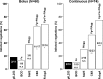
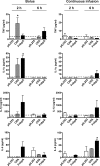
Animal models of infective endocarditis (IE) induced by high-grade bacteremia revealed the pathogenic roles of Staphylococcus aureus surface adhesins and platelet aggregation in the infection process. In humans, however, S. aureus IE possibly occurs through repeated bouts of low-grade bacteremia from a colonized site or intravenous device. Here we used a rat model of IE induced by continuous low-grade bacteremia to explore further the contributions of S. aureus virulence factors to the initiation of IE. Rats with aortic vegetations were inoculated by continuous intravenous infusion (0.0017 ml/min over 10 h) with 10(6) CFU of Lactococcus lactis pIL253 or a recombinant L. lactis strain expressing an individual S. aureus surface protein (ClfA, FnbpA, BCD, or SdrE) conferring a particular adhesive or platelet aggregation property. Vegetation infection was assessed 24 h later. Plasma was collected at 0, 2, and 6 h postinoculation to quantify the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin 1α (IL-1α), IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10. The percentage of vegetation infection relative to that with strain pIL253 (11%) increased when binding to fibrinogen was conferred on L. lactis (ClfA strain) (52%; P = 0.007) and increased further with adhesion to fibronectin (FnbpA strain) (75%; P < 0.001). Expression of fibronectin binding alone was not sufficient to induce IE (BCD strain) (10% of infection). Platelet aggregation increased the risk of vegetation infection (SdrE strain) (30%). Conferring adhesion to fibrinogen and fibronectin favored IL-1β and IL-6 production. Our results, with a model of IE induced by low-grade bacteremia, resembling human disease, extend the essential role of fibrinogen binding in the initiation of S. aureus IE. Triggering of platelet aggregation or an inflammatory response may contribute to or promote the development of IE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vaccination against Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis using recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing ClfA or FnbpA.Vaccine. 2015 Jul 9;33(30):3512-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.05.060. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26048778
-
Fibronectin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus mediate activation of human platelets via fibrinogen and fibronectin bridges to integrin GPIIb/IIIa and IgG binding to the FcgammaRIIa receptor.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jan;59(1):212-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04922.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16359330
-
Fibrinogen and fibronectin binding cooperate for valve infection and invasion in Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis.J Exp Med. 2005 May 16;201(10):1627-35. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050125. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 15897276 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-streptococcal interactions in endocarditis.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1996;7(3):222-36. doi: 10.1177/10454411960070030201. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1996. PMID: 8909879 Review.
-
The remarkably multifunctional fibronectin binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Dec;35(12):1923-1931. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2763-0. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27604831 Review.
Cited by
-
Aspirin plus ticlopidine prevented experimental endocarditis due to Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus gallolyticus.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv060. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv060. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26310867 Free PMC article.
-
Low efficacy of tobramycin in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;34(12):2349-57. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2488-5. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26440039
-
Infective endocarditis.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016 Sep 1;2:16059. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.59. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016. PMID: 27582414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal delivery of Lactococcus lactis carrying an anti-TNF scFv expression vector ameliorates experimental colitis in mice.BMC Biotechnol. 2019 Jun 25;19(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12896-019-0518-6. BMC Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31238939 Free PMC article.
-
Clumping factor A, von Willebrand factor-binding protein and von Willebrand factor anchor Staphylococcus aureus to the vessel wall.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 May;15(5):1009-1019. doi: 10.1111/jth.13653. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28182324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Que YA, Moreillon P. 2011. Infective endocarditis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 8:322–336 - PubMed
-
- Moreillon P, Que YA, Bayer AS. 2002. Pathogenesis of streptococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 16:297–318 - PubMed
-
- Foster TJ, Hook M. 1998. Surface protein adhesins of Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 6:484–488 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald JR, Foster TJ, Cox D. 2006. The interaction of bacterial pathogens with platelets. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4:445–457 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald JR, Loughman A, Keane F, Brennan M, Knobel M, Higgins J, Visai L, Speziale P, Cox D, Foster TJ. 2006. Fibronectin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus mediate activation of human platelets via fibrinogen and fibronectin bridges to integrin GPIIb/IIIa and IgG binding to the FcγRIIa receptor. Mol. Microbiol. 59:212–230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

