Protein translocation across the rough endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 23251026
- PMCID: PMC3552503
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013342
Protein translocation across the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
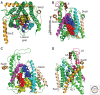
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a major site of protein biosynthesis in all eukaryotic cells, serving as the entry point for the secretory pathway and as the initial integration site for the majority of cellular integral membrane proteins. The core components of the protein translocation machinery have been identified, and high-resolution structures of the targeting components and the transport channel have been obtained. Research in this area is now focused on obtaining a better understanding of the molecular mechanism of protein translocation and membrane protein integration.
Figures


References
-
- Batey RT, Rambo RP, Lucast L, Rha B, Doudna JA 2000. Crystal structure of the ribonucleoprotein core of the signal recognition particle. Science 287: 1232–1239 - PubMed
-
- Beckmann R, Bubeck D, Grassucci R, Penczek P, Verschoor A, Blobel G, Frank J 1997. Alignment of conduits for the nascent polypeptide chain in the ribosome–Sec61 complex. Science 278: 2123–2126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
