Atomic model of the human cardiac muscle myosin filament
- PMID: 23251030
- PMCID: PMC3538242
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1212708110
Atomic model of the human cardiac muscle myosin filament
Abstract
Of all the myosin filaments in muscle, the most important in terms of human health, and so far the least studied, are those in the human heart. Here we report a 3D single-particle analysis of electron micrograph images of negatively stained myosin filaments isolated from human cardiac muscle in the normal (undiseased) relaxed state. The resulting 28-Å resolution 3D reconstruction shows axial and azimuthal (no radial) myosin head perturbations within the 429-Å axial repeat, with rotations between successive 132 Å-, 148 Å-, and 149 Å-spaced crowns of heads close to 60°, 35°, and 25° (all would be 40° in an unperturbed three-stranded helix). We have defined the myosin head atomic arrangements within the three crown levels and have modeled the organization of myosin subfragment 2 and the possible locations of the 39 Å-spaced domains of titin and the cardiac isoform of myosin-binding protein-C on the surface of the myosin filament backbone. Best fits were obtained with head conformations on all crowns close to the structure of the two-headed myosin molecule of vertebrate chicken smooth muscle in the dephosphorylated relaxed state. Individual crowns show differences in head-pair tilts and subfragment 2 orientations, which, together with the observed perturbations, result in different intercrown head interactions, including one not reported before. Analysis of the interactions between the myosin heads, the cardiac isoform of myosin-binding protein-C, and titin will aid in understanding of the structural effects of mutations in these proteins known to be associated with human cardiomyopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
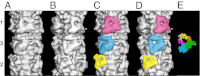

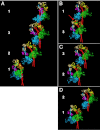
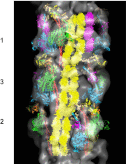
References
-
- Huxley HE. Electron microscope studies on the structure of natural and synthetic protein filaments from striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1963;7:281–308. - PubMed
-
- Squire JM. General model of myosin filament structure. II. Myosin filaments and cross-bridge interactions in vertebrate striated and insect flight muscles. J Mol Biol. 1972;72(1):125–138. - PubMed
-
- Labeit S, Kolmerer B. Titins: Giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science. 1995;270(5234):293–296. - PubMed
-
- Trinick J. Titin as a scaffold and spring. Cytoskeleton. Curr Biol. 1996;6(3):258–260. - PubMed
-
- Offer G, Moos C, Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973;74(4):653–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

