Effect of methylphenidate on sleep parameters in children with ADHD
- PMID: 23251204
- PMCID: PMC3521116
- DOI: 10.4306/pi.2012.9.4.384
Effect of methylphenidate on sleep parameters in children with ADHD
Abstract
Objective: The primary aim of this study was to investigate the acute impact of methylphenidate (MPH) on sleep parameters in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) children. The second aim was to investigate the different effects of intermediate- and longacting MPH on sleep parameters. The third aim was to test the different effects of dose and age on sleep parameters.
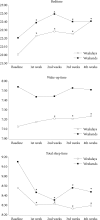
Methods: Ninety-three ADHD children were enrolled and randomized to two different MPH preparations. Baseline and daily sleep diaries were evaluated for four weeks after taking medication. Weekday and weekend bedtimes, wake-up times, sleep latencies and total sleep times were compared by weeks.
Results: After taking MPH, there was a significant delay in bedtimes and a significant reduction of total sleep time (TST) both on weekdays and at weekends. There was also a significant delay in wake-up time on weekdays. However, the difference was applied to younger age group children only. There was no difference in changes of TST between metadate-CD and OROS-MPH. There also was no difference in changes of TST with different doses of MPH.
Conclusion: MPH had negative impacts on sleep among young ADHD children, but different preparations and doses did not affect the result.
Keywords: ADHD; Children; Metadate-CD; Methylphenidate; OROS-MPH.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV TR. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Concannon PE, Tang YP. Management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a parental perspective. J Paediatr Child Health. 2005;41:625–630. - PubMed
-
- Capp PK, Pearl PL, Conlon C. Methylphenidate HCl: therapy for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2005;5:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Dulcan M. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children, adolescents, and adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36(10 Suppl):85S–121S. - PubMed
-
- Kratochvil CJ, Lake M, Pliszka SR, Walkup JT. Pharmacological management of treatment-induced insomnia in ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44:499–501. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources