Two types of Tet-On transgenic lines for doxycycline-inducible gene expression in zebrafish rod photoreceptors and a gateway-based tet-on toolkit
- PMID: 23251476
- PMCID: PMC3520995
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051270
Two types of Tet-On transgenic lines for doxycycline-inducible gene expression in zebrafish rod photoreceptors and a gateway-based tet-on toolkit
Abstract
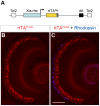
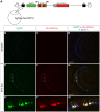
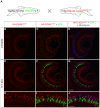
The ability to control transgene expression within specific tissues is an important tool for studying the molecular and cellular mechanisms of development, physiology, and disease. We developed a Tet-On system for spatial and temporal control of transgene expression in zebrafish rod photoreceptors. We generated two transgenic lines using the Xenopus rhodopsin promoter to drive the reverse tetracycline-controlled transcriptional transactivator (rtTA), one with self-reporting GFP activity and one with an epitope tagged rtTA. The self-reporting line includes a tetracycline response element (TRE)-driven GFP and, in the presence of doxycycline, expresses GFP in larval and adult rods. A time-course of doxycycline treatment demonstrates that maximal induction of GFP expression, as determined by the number of GFP-positive rods, is reached within approximately 24 hours of drug treatment. The epitope-tagged transgenic line eliminates the need for the self-reporting GFP activity by expressing a FLAG-tagged rtTA protein. Both lines demonstrate strong induction of TRE-driven transgenes from plasmids microinjected into one-cell embryos. These results show that spatial and temporal control of transgene expression can be achieved in rod photoreceptors. Additionally, system components are constructed in Gateway compatible vectors for the rapid cloning of doxycycline-inducible transgenes and use in other areas of zebrafish research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
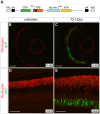
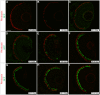
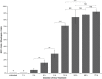
 ) The untreated and 1 h Dox-treated samples were quantified by counting the number of GFP-positive cells in all retinal sections from 10 eyes and dividing by an estimation of the total number of rods per eye. Statistical comparisons are indicated by brackets. ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; NS, not significant.
) The untreated and 1 h Dox-treated samples were quantified by counting the number of GFP-positive cells in all retinal sections from 10 eyes and dividing by an estimation of the total number of rods per eye. Statistical comparisons are indicated by brackets. ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; NS, not significant.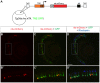
References
-
- Nasevicius A, Ekker SC (2000) Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’ in zebrafish. Nat Genet 26: 216–220. - PubMed
-
- Hans S, Freudenreich D, Geffarth M, Kaslin J, Machate A, et al. (2011) Generation of a non-leaky heat shock–inducible Cre line for conditional Cre/lox strategies in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 240: 108–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

