Decolourization of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis RKJ 700
- PMID: 23251673
- PMCID: PMC3520910
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052012
Decolourization of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis RKJ 700
Abstract
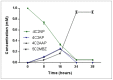
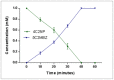
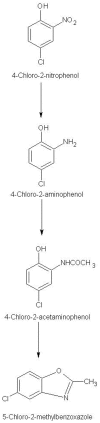
A 4-Chloro-2-nitrophenol (4C2NP) decolourizing strain RKJ 700 was isolated from soil collected from a pesticide contaminated site of India and identified as Bacillus subtilis on the basis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Bacillus subtilis RKJ 700 decolourized 4C2NP up to concentration of 1.5 mM in the presence of additional carbon source. The degradation pathway of 4C2NP was studied and 4-chloro-2-aminophenol, 4-chloro-2-acetaminophenol and 5-chloro-2-methylbenzoxazole (5C2MBZ) were identified as metabolites by high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Resting cell studies showed that Bacillus subtilis RKJ 700 depleted 4C2NP completely with stoichiometric formation of 5C2MBZ. This is the first report of (i) the degradation of 4C2NP at high concentration (1.5 mM) and, (ii) the formation of 5C2MBZ by a soil bacterium.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Arora PK, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (2012) Degradation of chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93: 2265–2267. - PubMed
-
- Saritha P, Aparna C, Himabindu V, Anjaneyulu Y (2007) Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of 4-chloro-2 nitrophenol. J Hazard Mater 149: 609–614. - PubMed
-
- Gharbani P, Khosravi M, Tabatabaii SM, Zare K, Dastmalchi S, et al. (2010) Degradation of trace aqueous 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol occurring in pharmaceutical industrial wastewater by ozone. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7: 377–384.
-
- Bruhn C, Bayly RC, Knackmus HJ (1988) The in vivo construction of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol assimilatory bacteria. Arch Microbiol 150: 171–177.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

