Genetic correction of human induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 23253609
- PMCID: PMC4722730
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004108
Genetic correction of human induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
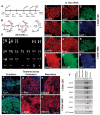
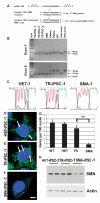
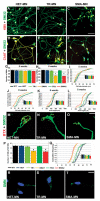
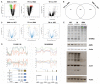
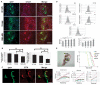
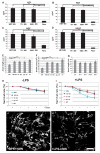
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is among the most common genetic neurological diseases that cause infant mortality. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generated from skin fibroblasts from SMA patients and genetically corrected have been proposed to be useful for autologous cell therapy. We generated iPSCs from SMA patients (SMA-iPSCs) using nonviral, nonintegrating episomal vectors and used a targeted gene correction approach based on single-stranded oligonucleotides to convert the survival motor neuron 2 (SMN2) gene into an SMN1-like gene. Corrected iPSC lines contained no exogenous sequences. Motor neurons formed by differentiation of uncorrected SMA-iPSCs reproduced disease-specific features. These features were ameliorated in motor neurons derived from genetically corrected SMA-iPSCs. The different gene splicing profile in SMA-iPSC motor neurons was rescued after genetic correction. The transplantation of corrected motor neurons derived from SMA-iPSCs into an SMA mouse model extended the life span of the animals and improved the disease phenotype. These results suggest that generating genetically corrected SMA-iPSCs and differentiating them into motor neurons may provide a source of motor neurons for therapeutic transplantation for SMA.
Figures
References
-
- Lefebvre S, Bürglen L, Reboullet S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, Benichou B, Cruaud C, Millasseau P, Zeviani M, Le Paslier D, Frézal J, Cohen D, Weissenbach J, Munnich A, Melki J. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995;80:155–165. - PubMed
-
- Coovert DD, Le TT, McAndrew PE, Strasswimmer J, Crawford TO, Mendell JR, Coulson SE, Androphy EJ, Prior TW, Burghes AH. The survival motor neuron protein in spinal muscular atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997;6:1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Crawford TO, Pardo CA. The neurobiology of childhood spinal muscular atrophy. Neurobiol. Dis. 1996;3:97–110. - PubMed
-
- Munsat TL, Davies KE. International SMA consortium meeting. (26-28 June 1992, Bonn, Germany) Neuromuscul. Disord. 1992;2:423–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

