Single real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection and quantification of genetically diverse HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor strains
- PMID: 23254130
- PMCID: PMC3592056
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02792-12
Single real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection and quantification of genetically diverse HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor strains
Abstract
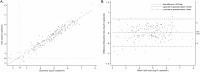
Although antiretroviral treatment availability has improved, the virological monitoring of patients remains largely uneven across regions. In addition, viral quantification tests are suffering from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) genetic diversity, fueled by the emergence of new recombinants and of lentiviruses from nonhuman primates. We developed a real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assay that is relatively inexpensive and able to detect and quantify all circulating forms of HIV-1 and its simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) precursors, SIVcpz and SIVgor. Primers and a probe were designed to detect all variants of the HIV-1/SIVcpz/SIVgor lineage. HIV-1 M plasma (n = 190; 1.68 to 7.78 log(10) copies/ml) representing eight subtypes, nine circulating recombinant forms, and 21 unique recombinant forms were tested. The mean PCR efficiency was 99%, with low coefficients of intra- and interassay variation (<5%) and a limit of quantification of <2.50 log(10) copies/ml, with a 200-μl plasma volume. On the studied range, the specificity and the analytical sensitivity were 100 and 97.4%, respectively. The viral loads were highly correlated (r = 0.95, P < 0.0001) with the reference method (generic HIV assay; Biocentric) and had no systematic difference, irrespective of genotype. Furthermore, 22 HIV-1 O plasmas were screened and were better quantified compared to the gold-standard RealTime HIV-1 assay (Abbott), including four samples that were only quantified by our assay. Finally, we could quantify SIVcpzPtt and SIVcpzPts from chimpanzee plasma (n = 5) and amplify SIVcpz and SIVgor from feces. Thus, the newly developed real-time RT-PCR assay detects and quantifies strains from the HIV-1/SIVcpz/SIVgor lineage, including a wide diversity of group M strains and HIV-1 O. It can therefore be useful in geographical areas of high HIV diversity and at risk for the emergence of new HIV variants.
Figures

References
-
- Fiscus SA, Cheng B, Crowe SM, Demeter L, Jennings C, Miller V, Respess R, Stevens W. 2006. HIV-1 viral load assays for resource-limited settings. PLoS Med. 3:e417 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030417 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonard D, Rouet F, Toni TA, Minga A, Huet C, Ekouevi DK, Dabis F, Salamon R, Rouzioux C. 2003. Field evaluation of an improved assay using a heat-dissociated p24 antigen for adults mainly infected with HIV-1 CRF02_AG strains in Cote d'Ivoire, West Africa. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 34:267–273 - PubMed
-
- Ribas SG, Ondoa P, Schupbach J, van der Groen G, Fransen K. 2003. Performance of a quantitative human immunodeficiency virus type 1 p24 antigen assay on various HIV-1 subtypes for the follow-up of human immunodeficiency type 1 seropositive individuals. J. Virol. Methods 113:29–34 - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Plantier JC, Hellot MF, Tuaillon E, Gueudin M, Damond F, Malmsten A, Corrigan GE, Simon F. 2003. A new quantitative HIV load assay based on plasma virion reverse transcriptase activity for the different types, groups and subtypes. AIDS 17:331–336 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

