Rapid identification of bacteria and yeasts from positive-blood-culture bottles by using a lysis-filtration method and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrum analysis with the SARAMIS database
- PMID: 23254131
- PMCID: PMC3592086
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02326-12
Rapid identification of bacteria and yeasts from positive-blood-culture bottles by using a lysis-filtration method and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrum analysis with the SARAMIS database
Abstract
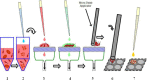
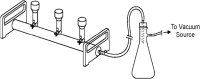
Rapid identification of microorganisms causing bloodstream infections directly from a positive blood culture would decrease the time to directed antimicrobial therapy and greatly improve patient care. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) is a fast and reliable method for identifying microorganisms from positive culture. This study evaluates the performance of a novel filtration-based method for processing positive-blood-culture broth for immediate identification of microorganisms by MALDI-TOF with a Vitek MS research-use-only system (VMS). BacT/Alert non-charcoal-based blood culture bottles that were flagged positive by the BacT/Alert 3D system were included. An aliquot of positive-blood-culture broth was incubated with lysis buffer for 2 to 4 min at room temperature, the resulting lysate was filtered through a membrane, and harvested microorganisms were identified by VMS. Of the 259 bottles included in the study, VMS identified the organisms in 189 (73%) cultures to the species level and 51 (19.7%) gave no identification (ID), while 6 (2.3%) gave identifications that were considered incorrect. Among 131 monomicrobic isolates from positive-blood-culture bottles with one spot having a score of 99.9%, the IDs for 131 (100%) were correct to the species level. In 202 bottles where VMS was able to generate an ID, the IDs for 189 (93.6%) were correct to the species level, whereas the IDs provided for 7 isolates (3.5%) were incorrect. In conclusion, this method does not require centrifugation and produces a clean spectrum for VMS analysis in less than 15 min. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of the new lysis-filtration method for identifying microorganisms directly from positive-blood-culture bottles in a clinical setting.
Figures
References
-
- Cherkaoui A, Hibbs J, Emonet S, Tangomo M, Girard M, Francois P, Schrenzel J. 2010. Comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry methods with conventional phenotypic identification for routine identification of bacteria to the species level. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48:1169–1175 - PMC - PubMed
-
- La Scola B, Raoult D. 2009. direct identification of bacteria in positive blood culture bottles by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS One 4:e8041 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christner M, Rohde H, Wolters M, Sobottka I, Wegscheider K, Aepfelbacher M. 2010. Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption–ionization time of flight mass spectrometry fingerprinting. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48:1584–1591 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

