The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target
- PMID: 23254192
- PMCID: PMC4295774
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3406
The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target
Abstract
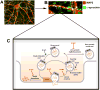
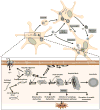
Disorders characterized by α-synuclein (α-syn) accumulation, Lewy body formation and parkinsonism (and in some cases dementia) are collectively known as Lewy body diseases. The molecular mechanism (or mechanisms) through which α-syn abnormally accumulates and contributes to neurodegeneration in these disorders remains unknown. Here, we provide an overview of current knowledge and prevailing hypotheses regarding the conformational, oligomerization and aggregation states of α-syn and their role in regulating α-syn function in health and disease. Understanding the nature of the various α-syn structures, how they are formed and their relative contributions to α-syn-mediated toxicity may inform future studies aiming to develop therapeutic prevention and intervention.
Figures
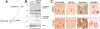
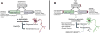
References
-
- McKeith IG, et al. Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology. 1996;47:1113–1124. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Pathoanatomy of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol. 2000;247 Suppl 2:II3–II10. Detailed description of the pathoanatomy that occurs in Parkinson's disease. - PubMed
-
- Vekrellis K, Xilouri M, Emmanouilidou E, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L. Pathological roles of alpha-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:1015–1025. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1167–1169. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

