KSGal6ST generates galactose-6-O-sulfate in high endothelial venules but does not contribute to L-selectin-dependent lymphocyte homing
- PMID: 23254996
- PMCID: PMC3555504
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cws166
KSGal6ST generates galactose-6-O-sulfate in high endothelial venules but does not contribute to L-selectin-dependent lymphocyte homing
Abstract
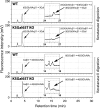
The addition of sulfate to glycan structures can regulate their ability to serve as ligands for glycan-binding proteins. Although sulfate groups present on the monosaccharides glucosamine, uronate, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine are recognized by defined receptors that mediate important functions, the functional significance of galactose-6-O-sulfate (Gal6S) is not known. However, in vitro studies using synthetic glycans and sulfotransferase overexpression implicate Gal6S as a binding determinant for the lymphocyte homing receptor, L-selectin. Only two sulfotransferases have been shown to generate Gal6S, namely keratan sulfate galactose 6-O-sulfotransferase (KSGal6ST) and chondroitin 6-O-sulfotransferase-1 (C6ST-1). In the present study, we use mice deficient in KSGal6ST and C6ST-1 to test whether Gal6S contributes to ligand recognition by L-selectin in vivo. First, we establish that KSGal6ST is selectively expressed in high endothelial venules (HEVs) in lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. We also determine by mass spectrometry that KSGal6ST generates Gal6S on several classes of O-glycans in peripheral lymph nodes. Furthermore, KSGal6ST, but not C6ST-1, is required for the generation of the Gal6S-containing glycan, 6,6'-disulfo-3'sLN (Siaα2→3[6S]Galβ1→4[6S]GlcNAc) or a closely related structure in lymph node HEVs. Nevertheless, L-selectin-dependent short-term homing of lymphocytes is normal in KSGal6ST-deficient mice, indicating that the Gal6S-containing structures we detected do not contribute to L-selectin ligand recognition in this setting. These results refine our understanding of the biological ligands for L-selectin and introduce a mouse model for investigating the functions of Gal6S in other contexts.
Figures





References
-
- Akama TO, Nishida K, Nakayama J, Watanabe H, Ozaki K, Nakamura T, Dota A, Kawasaki S, Inoue Y, Maeda N, et al. Macular corneal dystrophy type I and type II are caused by distinct mutations in a new sulphotransferase gene. Nat Genet. 2000;26:237–241. doi:10.1038/79987. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arata-Kawai H, Singer MS, Bistrup A, Zante A, Wang YQ, Ito Y, Bao X, Hemmerich S, Fukuda M, Rosen SD. Functional contributions of N- and O-glycans to L-selectin ligands in murine and human lymphoid organs. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:423–433. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arbones ML, Ord DC, Ley K, Ratech H, Maynard-Curry C, Otten G, Capon DJ, Tedder TF. Lymphocyte homing and leukocyte rolling and migration are impaired in L-selectin-deficient mice. Immunity. 1994;1:247–260. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(94)90076-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baenziger JU. Glycoprotein hormone GalNAc-4-sulphotransferase. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:326–330. doi:10.1042/BST0310326. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bertozzi CR, Fukuda S, Rosen SD. Sulfated disaccharide inhibitors of L-selectin: Deriving structural leads from a physiological selectin ligand. Biochemistry. 1995;34:14271–14278. doi:10.1021/bi00044a001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

