JNK and STAT3 signaling pathways converge on Akt-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 in bronchial epithelial cells induced by arsenic
- PMID: 23255093
- PMCID: PMC3570498
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.23030
JNK and STAT3 signaling pathways converge on Akt-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 in bronchial epithelial cells induced by arsenic
Abstract
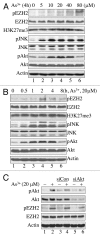
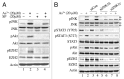
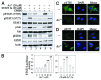
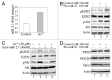
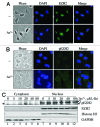
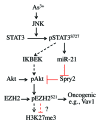
The molecular mechanisms by which arsenic (As ( 3+) ) causes human cancers remain to be fully elucidated. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is the catalytic subunit of polycomb-repressive complexes 2 (PRC2) that promotes trimethylation of lysine 27 of histone H3, leading to altered expression of tumor suppressors or oncogenes. In the present study, we determined the effect of As ( 3+) on EZH2 phosphorylation and the signaling pathways important for As ( 3+) -induced EZH2 phosphorylation in human bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B. The involvement of kinases in As ( 3+) -induced EZH2 phosphorylation was validated by siRNA-based gene silencing. The data showed that As ( 3+) can induce phosphorylation of EZH2 at serine 21 in human bronchial epithelial cells and that the phosphorylation of EZH2 requires an As ( 3+) -activated signaling cascade from JNK and STAT3 to Akt. Transfection of the cells with siRNA specific for JNK1 revealed that JNK silencing reduced serine727 phosphorylation of STAT3, Akt activation and EZH2 phosphorylation, suggesting that JNK is the upstream kinase involved in As ( 3+) -induced EZH2 phosphorylation. Because As ( 3+) is capable of inducing miRNA-21 (miR-21), a STAT3-regulated miRNA that represses protein translation of PTEN or Spry2, we also tested the role of STAT3 and miR-21 in As ( 3+) -induced EZH2 phosphorylation. Ectopic overexpression of miR-21 promoted Akt activation and phosphorylation of EZH2, whereas inhibiting miR-21 by transfecting the cells with anti-miR-21 inhibited Akt activation and EZH2 phosphorylation. Taken together, these results demonstrate a contribution of the JNK, STAT3 and Akt signaling axis to As ( 3+) -induced EZH2 phosphorylation. Importantly, these findings may reveal new molecular mechanisms underlying As ( 3+) -induced carcinogenesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Linking JNK-STAT3-Akt signaling axis to EZH2 phosphorylation: a novel pathway of carcinogenesis.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 15;12(2):202-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.23419. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23287465 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, et al. Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol. 2011;31:95–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
