MicroRNAs and DNA damage response: implications for cancer therapy
- PMID: 23255103
- PMCID: PMC3570514
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.23051
MicroRNAs and DNA damage response: implications for cancer therapy
Abstract
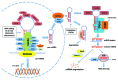
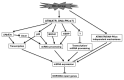
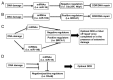
The DNA damage response (DDR) pathways play critical roles in protecting the genome from DNA damage. Abrogation of DDR often results in elevated genomic instability and cellular sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. Many proteins involved in DDR are subjected to precise regulation at multiple levels, such as transcriptional control and posttranslational modifications, in response to DNA damage. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. The expression levels of some miRNAs change in response to DNA damage. Some miRNAs, such as miR-24, 138, 96 and 182, have been implicated in DDR and/or DNA repair and affect cellular sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. In this review, we summarize recent findings related to the emerging roles of miRNAs in regulating DDR and DNA repair and discuss their potential in cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posttranscriptional regulation of miRNAs in the DNA damage response.RNA Biol. 2011 Nov-Dec;8(6):960-3. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.6.17337. Epub 2011 Nov 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21941125 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in DNA Damage Response: Opportunities for Cancer Therapeutics.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1699:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7435-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29086365
-
DNA lesions and DNA damage response: even long lasting relationships need a "break".Cell Cycle. 2008 Dec;7(23):3653-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.23.7178. Epub 2008 Dec 13. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19029795
-
MicroRNAs, DNA Damage Response, and Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 12;17(12):2087. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122087. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27973455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage response pathways in tumor suppression and cancer treatment.World J Surg. 2009 Apr;33(4):661-6. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9840-1. World J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19034564 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-29a regulates the benzo[a]pyrene dihydrodiol epoxide-induced DNA damage response through Cdc7 kinase in lung cancer cells.Oncogenesis. 2013 Jul 22;2(7):e57. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2013.20. Oncogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23877787 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of artificial MiRNA mimics with centered-site complementarity for gene targeting.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072062. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013456 Free PMC article.
-
Differential miRNA expression profiling reveals miR-205-3p to be a potential radiosensitizer for low- dose ionizing radiation in DLD-1 cells.Oncotarget. 2018 May 29;9(41):26387-26405. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25405. eCollection 2018 May 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29899866 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between PTEN/PI3K/Akt Signalling and DNA Damage in the Oocyte: Implications for Primordial Follicle Activation, Oocyte Quality and Ageing.Cells. 2020 Jan 14;9(1):200. doi: 10.3390/cells9010200. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31947601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid inhibits growth of head and neck cancer cell lines by reactivation of tumor suppressor microRNAs.Oral Oncol. 2016 May;56:32-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27086484 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
