Cellular entry of human papillomavirus type 16 involves activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway and inhibition of autophagy
- PMID: 23255786
- PMCID: PMC3571372
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02319-12
Cellular entry of human papillomavirus type 16 involves activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway and inhibition of autophagy
Abstract
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) in the growth factor receptor (GFR) pathway is a crucial metabolic sensor that integrates growth factor signals in cells. We recently showed that human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 exposure activates signaling from GFRs in human keratinocytes. Thus, we predicted that the virus would induce the PI3K/mTOR pathway upon interaction with host cells. We detected activation of Akt and mTOR several minutes following exposure of human keratinocytes to HPV type 16 (HPV16) pseudovirions. Activated mTOR induced phosphorylation of the mTOR complex 1 substrates 4E-BP1 and S6K, which led to induction of the functional protein translational machinery. Blockade of epidermal GFR (EGFR) signaling revealed that each of these events is at least partially dependent upon EGFR activation. Importantly, activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling inhibited autophagy in the early stages of virus-host cell interaction. Biochemical and genetic approaches revealed critical roles for mTOR activation and autophagy suppression in HPV16 early infection events. In summary, the HPV-host cell interaction stimulates the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and inhibits autophagy, and in combination these events benefit virus infection.
Figures


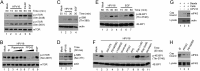
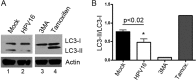
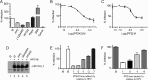

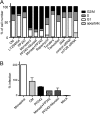
Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by a dietary flavonoid fisetin.Int J Cancer. 2012 Apr 1;130(7):1695-705. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26178. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21618507 Free PMC article.
-
Paradigm of kinase-driven pathway downstream of epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt in human lung carcinomas.Hum Pathol. 2011 Feb;42(2):214-26. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.05.025. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Hum Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21040950
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in breast cancer.Oncologist. 2011;16(4):404-14. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0402. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 21406469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori promotes eukaryotic protein translation by activating phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/mTOR.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;55:157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.08.023. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25194338
-
Targeting the translational apparatus to improve leukemia therapy: roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.Leukemia. 2011 Jul;25(7):1064-79. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.46. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21436840 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Modulators of Autophagy as a Potential Strategy for the Treatment of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4067. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084067. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MARCH2 regulates autophagy by promoting CFTR ubiquitination and degradation and PIK3CA-AKT-MTOR signaling.Autophagy. 2016 Sep;12(9):1614-30. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1192752. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27308891 Free PMC article.
-
The Known and Potential Intersections of Rab-GTPases in Human Papillomavirus Infections.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Aug 14;7:139. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00139. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31475144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human DNA Virus Exploitation of the MAPK-ERK Cascade.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 12;20(14):3427. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143427. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reverse-phase protein array profiling of oropharyngeal cancer and significance of PIK3CA mutations in HPV-associated head and neck cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 May 1;20(9):2300-11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2585. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24599934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surviladze Z, Dziduszko A, Ozbun MA. 2012. Essential roles for soluble virion-associated heparan sulfonated proteoglycans and growth factors in human papillomavirus infections. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1002519 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002519 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq JM, Hemmings BA. 1997. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31515–31524 - PubMed
-
- Cooray S. 2004. The pivotal role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signal transduction in virus survival. J. Gen. Virol. 85:1065–1076 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

