Biodistribution and dosimetry of (177)Lu-tetulomab, a new radioimmunoconjugate for treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 23256748
- PMCID: PMC3624777
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471011306010004
Biodistribution and dosimetry of (177)Lu-tetulomab, a new radioimmunoconjugate for treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
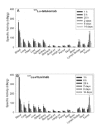
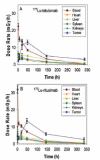
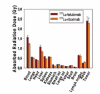
The biodistribution of the anti-CD37 radioimmunoconjugate (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab ((177)Lu-DOTA-HH1) was evaluated. Biodistribution of (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab was compared with (177)Lu-tetraxetan-rituximab and free (177)Lu in nude mice implanted with Daudi lymphoma xenografts. The data showed that (177)Lu-tetulomab had a relevant stability and tumor targeting properties in the human lymphoma model. The half-life of (177)Lu allowed significant tumor to normal tissue ratios to be obtained indicating that (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab could be suitable for clinical testing. The biological and effective half-life in blood was higher for (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab than for (177)Lu-tetraxetan-rituximab. The biodistribution of (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab did not change significantly when the protein dose was varied from 0.01 to 1 mg/kg. Dosimetry calculations showed that the absorbed radiation doses to normal tissues and tumor in mice were not significantly different for (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetuloma b and (177)Lu-tetraxetan-rituximab. The absorbed radiation doses were extrapolated to human absorbed radiation doses. These extrapolated absorbed radiation doses to normal tissues for (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab at an injection of 40 MBq/kg were significantly lower than the absorbed radiation doses for 15 MBq/kg Zevalin, suggesting that higher tumor radiation dose can be reached with (177)Lu-tetraxetan-tetulomab in the clinic.
Figures
References
-
- Foran JM, Norton AJ, Micallef IN, Taussig DC, Amess JA, Rohatiner AZ, Lister TA. Loss of CD20 expression following treatment with rituximab (chimaeric monoclonal anti-CD20) a retrospective cohort analysis. Br. J. Haematol . 2001;114(4 ):881–883. - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto T, Tomita A, Hiraga J, Shimada K, Kiyoi H, Kinoshita T, Naoe T. Escape mechanisms from antibody therapy to lymphoma cells downregulation of CD20 mRNA by recruitment of the HDAC complex and not by DNA methylation. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun . 2009;390(1 ):48–53. - PubMed
-
- Wada N, Kohara M, Ogawa H, Sugiyama H, Fukuhara S, Tatsumi Y, Kanamaru A, Hino M, Kanakura Y, Morii E, Aozasa K. Change of CD20 Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Rituximab, an Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody: A Study of the Osaka Lymphoma Study Group. Case. Rep. Oncol . 2009;2(3 ):194–202. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moldenhauer G. CD37. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2000;14(4 ):281–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
