Hepatic sinusoidal endothelium avidly binds platelets in an integrin-dependent manner, leading to platelet and endothelial activation and leukocyte recruitment
- PMID: 23257923
- PMCID: PMC3602682
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00407.2012
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelium avidly binds platelets in an integrin-dependent manner, leading to platelet and endothelial activation and leukocyte recruitment
Abstract
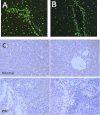
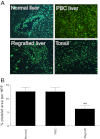
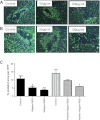
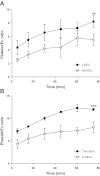
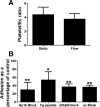
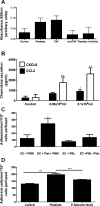
Platelets have recently been shown to drive liver injury in murine models of viral hepatitis and promote liver regeneration through the release of serotonin. Despite their emerging role in inflammatory liver disease, little is known about the mechanisms by which platelets bind to the hepatic vasculature. Therefore, we referenced public expression data to determine the profile of potential adhesive receptors expressed by hepatic endothelium. We then used a combination of tissue-binding and flow-based endothelial-binding adhesion assays to show that resting platelets bind to human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells and that the magnitude of adhesion is greatly enhanced by thrombin-induced platelet activation. Adhesion was mediated by the integrins Gp1b, αIIbβIII, and αvβ3, as well as immobilized fibrinogen. Platelet binding to hepatic endothelial cells resulted in NF-κB activation and increased chemokine secretion. The functional relevance of platelet binding was confirmed by experiments that showed markedly increased binding of neutrophils and lymphocytes to hepatic endothelial cells under shear conditions replicating those found in the hepatic sinusoid, which was in part dependent on P-selectin expression. Thus the ability of platelets to activate endothelium and promote leukocyte adhesion may reflect an additional mechanism through which they promote liver injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adhesion of activated platelets to endothelial cells: evidence for a GPIIbIIIa-dependent bridging mechanism and novel roles for endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), alphavbeta3 integrin, and GPIbalpha.J Exp Med. 1998 Feb 2;187(3):329-39. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.3.329. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9449713 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets induce alterations of chemotactic and adhesive properties of endothelial cells mediated through an interleukin-1-dependent mechanism. Implications for atherogenesis.Atherosclerosis. 2000 Jan;148(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00241-5. Atherosclerosis. 2000. PMID: 10580173
-
Activation of vascular adhesion protein-1 on liver endothelium results in an NF-kappaB-dependent increase in lymphocyte adhesion.Hepatology. 2007 Feb;45(2):465-74. doi: 10.1002/hep.21497. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17256751
-
Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: role of integrins and their ligands.Transfus Apher Sci. 2003 Jun;28(3):257-64. doi: 10.1016/S1473-0502(03)00044-2. Transfus Apher Sci. 2003. PMID: 12725952 Review.
-
[Platelet--vessel wall interactions].Therapie. 2006 Sep-Oct;61(5):371-8. doi: 10.2515/therapie:2006068. Therapie. 2006. PMID: 17243265 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Interactions with Asialo-Glycoprotein Receptors and Platelets Are Dispensable for CD8+ T Cell Localization in the Murine Liver.J Immunol. 2022 Jun 15;208(12):2738-2748. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101037. Epub 2022 Jun 1. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35649630 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;12(3):641. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030641. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of depression and antidepressant usage on primary biliary cholangitis clinical outcomes.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 4;13(4):e0194839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194839. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29617396 Free PMC article.
-
Hemostasis and Liver Regeneration.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020 Sep;46(6):735-742. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1715450. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32906177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sanguineous normothermic machine perfusion improves hemodynamics and biliary epithelial regeneration in donation after cardiac death porcine livers.Liver Transpl. 2014 Aug;20(8):987-99. doi: 10.1002/lt.23906. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Liver Transpl. 2014. PMID: 24805852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DH, Hubscher SG, Fisher NC, Williams A, Robinson M. Expression of E-selectin and E-selectin ligands in human liver inflammation. Hepatology 24: 533–538, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F, Pujol-Borrell R. Lymphoid neogenesis in chronic inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 6: 205–217, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Beacham DA, Tran LP, Shapiro SS. Cytokine treatment of endothelial cells increases glycoprotein Ib alpha-dependent adhesion to von Willebrand factor. Blood 89: 4071–4077, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Bennett JS, Chan C, Vilaire G, Mousa SA, DeGrado WF. Agonist activated àvá3 on platelets and lymphocytes binds to the matrix protein osteopontin. J Biol Chem 272: 8137–8140, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Boerma MKJ, van Loenen M, Klein HR, Bart CI, Zurcher C, Wondergem J. Increased deposition of von Willebrand factor in the rat heart after local ionizing irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol 180: 8, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

