Iron binding activity is essential for the function of IscA in iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis
- PMID: 23258274
- PMCID: PMC3569480
- DOI: 10.1039/c2dt32000b
Iron binding activity is essential for the function of IscA in iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis
Abstract
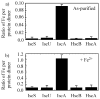
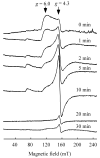
Iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis requires coordinated delivery of iron and sulphur to scaffold proteins, followed by transfer of the assembled clusters from scaffold proteins to target proteins. This complex process is accomplished by a group of dedicated iron-sulphur cluster assembly proteins that are conserved from bacteria to humans. While sulphur in iron-sulphur clusters is provided by L-cysteine via cysteine desulfurase, the iron donor(s) for iron-sulphur cluster assembly remains largely elusive. Here we report that among the primary iron-sulphur cluster assembly proteins, IscA has a unique and strong binding activity for mononuclear iron in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, the ferric iron centre tightly bound in IscA can be readily extruded by l-cysteine, followed by reduction to ferrous iron for iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis. Substitution of the highly conserved residue tyrosine 40 with phenylalanine (Y40F) in IscA results in a mutant protein that has a diminished iron binding affinity but retains the iron-sulphur cluster binding activity. Genetic complementation studies show that the IscA Y40F mutant is inactive in vivo, suggesting that the iron binding activity is essential for the function of IscA in iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mobilization of the iron centre in IscA for the iron-sulphur cluster assembly in IscU.Biochem J. 2005 Aug 1;389(Pt 3):797-802. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050405. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15828873 Free PMC article.
-
Copper binding in IscA inhibits iron-sulphur cluster assembly in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Aug;93(4):629-44. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12676. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24946160 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary roles of SufA and IscA in the biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters in Escherichia coli.Biochem J. 2008 Jan 15;409(2):535-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071166. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 17941825
-
Iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis via the SUF pathway.Metallomics. 2018 Aug 15;10(8):1038-1052. doi: 10.1039/c8mt00150b. Metallomics. 2018. PMID: 30019043 Review.
-
Interplay between oxygen and Fe-S cluster biogenesis: insights from the Suf pathway.Biochemistry. 2014 Sep 23;53(37):5834-47. doi: 10.1021/bi500488r. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25153801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fe-S cluster biogenesis by the bacterial Suf pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Nov;1867(11):118829. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118829. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32822728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron-Sulfur Cluster Biogenesis and Iron Homeostasis in Cyanobacteria.Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 28;11:165. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00165. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32184761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards magnetism in pigeon MagR: Iron- and iron-sulfur binding work indispensably and synergistically.Zool Res. 2023 Jan 18;44(1):142-152. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.423. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 36484226 Free PMC article.
-
On the evolutionary trail of MagRs.Zool Res. 2024 Jul 18;45(4):821-830. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.074. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38894524 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected divergence in magnetoreceptor MagR from robin and pigeon linked to two sequence variations.Zool Res. 2024 Jan 18;45(1):69-78. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.138. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38114434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beinert H, Holm RH, Munck E. Science. 1997;277:653–659. - PubMed
-
- Lill R. Nature. 2009;460:831–838. - PubMed
-
- White MF, Dillingham MS. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 2012;22:94–100. - PubMed
-
- Crack JC, Green J, Thomson AJ, Le Brun NE. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2012;16:35–44. - PubMed
-
- Zheng L, Cash VL, Flint DH, Dean DR. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13264–13272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

