Prognostication in eye cancer: the latest tumor, node, metastasis classification and beyond
- PMID: 23258307
- PMCID: PMC3574256
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2012.256
Prognostication in eye cancer: the latest tumor, node, metastasis classification and beyond
Abstract
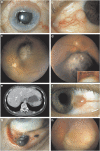
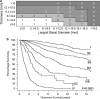
The tumour, node, metastasis (TNM) classification is a universal cancer staging system, which has been used for five decades. The current seventh edition became effective in 2010 and covers six ophthalmic sites: eyelids, conjunctiva, uvea, retina, orbit, and lacrimal gland; and five cancer types: carcinoma, sarcoma, melanoma, retinoblastoma, and lymphoma. The TNM categories are based on the anatomic extent of the primary tumour (T), regional lymph node metastases (N), and systemic metastases (M). The T categories of ophthalmic cancers are based on the size of the primary tumour and any invasion of periocular structures. The anatomic category is used to determine the TNM stage that correlates with survival. Such staging is currently implemented only for carcinoma of the eyelid and melanoma of the uvea. The classification of ciliary body and choroidal melanoma is the only one based on clinical evidence so far: a database of 7369 patients analysed by the European Ophthalmic Oncology Group. It spans a prognosis from 96% 5-year survival for stage I to 97% 5-year mortality for stage IV. The most accurate criterion for prognostication in uveal melanoma is, however, analysis of chromosomal alterations and gene expression. When such data are available, the TNM stage may be used for further stratification. Prognosis in retinoblastoma is frequently assigned by using an international classification, which predicts conservation of the eye and vision, and an international staging separate from the TNM system, which predicts survival. The TNM cancer staging manual is a useful tool for all ophthalmologists managing eye cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Sobin LH. TNM: evolution and relation to other prognostic factors. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003;21:3–7. - PubMed
-
- TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours5th ed.Wiley: New York; 1997
-
- TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours6th ed.Wiley-Liss: New York; 2002
-
- Finger PT. Do you speak ocular tumor. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:13–14. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Buzaid AC, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, et al. An evidence-based staging system for cutaneous melanoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:131–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

