Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA
- PMID: 23258412
- PMCID: PMC3855410
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1229963
Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA
Abstract
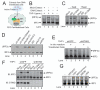
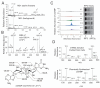
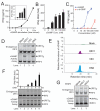
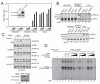
Cytosolic DNA induces type I interferons and other cytokines that are important for antimicrobial defense but can also result in autoimmunity. This DNA signaling pathway requires the adaptor protein STING and the transcription factor IRF3, but the mechanism of DNA sensing is unclear. We found that mammalian cytosolic extracts synthesized cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic GMP-AMP, or cGAMP) in vitro from adenosine triphosphate and guanosine triphosphate in the presence of DNA but not RNA. DNA transfection or DNA virus infection of mammalian cells also triggered cGAMP production. cGAMP bound to STING, leading to the activation of IRF3 and induction of interferon-β. Thus, cGAMP functions as an endogenous second messenger in metazoans and triggers interferon production in response to cytosolic DNA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunology. Sensing the dark side of DNA.Science. 2013 Feb 15;339(6121):763-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1234724. Science. 2013. PMID: 23413341 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

