Acute-phase inflammatory response in idiopathic sudden deafness: pathogenic implications
- PMID: 23258981
- PMCID: PMC3508735
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/216592
Acute-phase inflammatory response in idiopathic sudden deafness: pathogenic implications
Abstract
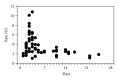
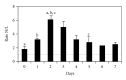
The acute-phase inflammatory response in the peripheral bloodstream can be an expression of transient cerebral ischaemia in idiopathic sudden deafness. For this, a neurological and otorhinolaryngological examination of each patient, performing tests on audiometry, and tympanometry, haemogram, and cranial magnetic resonance were performed. The acute-phase inflammatory response manifests as an increased neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio that is detected 48-72 hours after the appearance of sudden deafness. This study shows that there is an acute-phase response in the peripheral bloodstream with an increased neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as an expression of an inflammatory process that can be caused by transient cerebral ischaemia in sudden deafness. In addition, the increased neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio can rule out a viral origin of sudden deafness, since a viral infection lowers the neutrophil count and increases the lymphocyte count, thus reducing the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. These findings aid in understanding the pathogenic mechanisms involved in sudden deafness and offer better treatment to the patient.
Figures
References
-
- Schreiber BE, Agrup C, Haskard DO, Luxon LM. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. The Lancet. 2010;375(9721):1203–1211. - PubMed
-
- Lee H, Ahn BH, Baloh RW. Sudden deafness with vertigo as a sole manifestation of anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2004;222(1-2):105–107. - PubMed
-
- Murakami T, Nakayasu H, Doi M, et al. Anterior and posterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction with sudden deafness and vertigo. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 2006;13(10):1051–1054. - PubMed
-
- Son EJ, Bang JH, Kang JG. Anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction presenting with sudden hearing loss and vertigo. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(3):556–558. - PubMed
-
- Gerace C, Pianura C. Sudden deafness without vertigo as a sole manifestation of AICA infarct. Neurological Sciences. 2008;29(5):371–372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

