A continuous semantic space describes the representation of thousands of object and action categories across the human brain
- PMID: 23259955
- PMCID: PMC3556488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.014
A continuous semantic space describes the representation of thousands of object and action categories across the human brain
Abstract
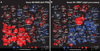
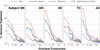
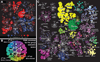
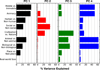
Humans can see and name thousands of distinct object and action categories, so it is unlikely that each category is represented in a distinct brain area. A more efficient scheme would be to represent categories as locations in a continuous semantic space mapped smoothly across the cortical surface. To search for such a space, we used fMRI to measure human brain activity evoked by natural movies. We then used voxelwise models to examine the cortical representation of 1,705 object and action categories. The first few dimensions of the underlying semantic space were recovered from the fit models by principal components analysis. Projection of the recovered semantic space onto cortical flat maps shows that semantic selectivity is organized into smooth gradients that cover much of visual and nonvisual cortex. Furthermore, both the recovered semantic space and the cortical organization of the space are shared across different individuals.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


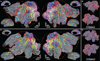

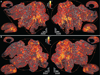
References
-
- Adelson EH, Bergen JR. Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. J Opt Soc Am A. 1985;2(2):284–299. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre GK, Zarahn E, D’esposito M. An Area within Human Ventral Cortex Sensitive to Building Stimuli: Evidence and Implications. Neuron. 1998;21(2):373–383. - PubMed
-
- Avidan, Hasson U, Malach R, Behrmann M. Detailed exploration of face-related processing in congenital prosopagnosia 2. Functional neuroimaging findings. J Cogn Neurosci. 2005;17(7):1150–1167. - PubMed
-
- Buccino G, Binkofski F, Fink GR, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Gallese V, Seitz RJ, et al. Action observation activates premotor and parietal areas in a somatotopic manner: an fMRI study. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13(2):400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

