Conformational free-energy landscapes for a peptide in saline environments
- PMID: 23260053
- PMCID: PMC3525846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.001
Conformational free-energy landscapes for a peptide in saline environments
Abstract
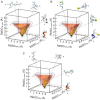
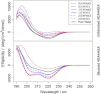
The conformations that proteins adopt in solution are a function of both their primary structure and surrounding aqueous environment. Recent experimental and computational work on small peptides, e.g., polyK, polyE, and polyR, have highlighted an interesting and unusual behavior in the presence of aqueous ions such as ClO₄⁻, Na⁺, and K⁺. Notwithstanding the aforementioned studies, as of this writing, the nature of the driving force induced by the presence of ions and its role on the conformational stability of peptides remains only partially understood. Molecular-dynamics simulations have been performed on the heptapeptide AEAAAEA in NaCl and KCl solutions at concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 M. Metadynamics in conjunction with a three-dimensional model reaction coordinate was used to sample the conformational space of the peptide. All simulations were run for 2 μs. Free-energy landscapes were computed over the model reaction coordinate for the peptide in each saline assay as well as in the absence of ions. Circular dichroism spectra were also calculated from each trajectory. In the presence of Na⁺ and K⁺ ions, no increase in helicity is observed with respect to the conformation in pure water.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salt-specific stability and denaturation of a short salt-bridge-forming alpha-helix.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Oct 22;130(42):14000-7. doi: 10.1021/ja805562g. Epub 2008 Sep 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18821757
-
Supercooling of aqueous NaCl and KCl solutions under acoustic levitation.J Chem Phys. 2006 Oct 14;125(14):144503. doi: 10.1063/1.2358134. J Chem Phys. 2006. PMID: 17042605
-
The impact of monovalent ion force field model in nucleic acids simulations.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009 Dec 7;11(45):10596-607. doi: 10.1039/b912067j. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 20145804
-
Helix formation by alanine-based peptides in pure water and electrolyte solutions: insights from molecular dynamics simulations.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Aug 29;117(34):9866-76. doi: 10.1021/jp406231g. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23919617
-
[A turning point in the knowledge of the structure-function-activity relations of elastin].J Soc Biol. 2001;195(2):181-93. J Soc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11727705 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Thermodynamics of Deca-alanine Folding in Water.J Chem Theory Comput. 2014 Jul 8;10(7):2836-2844. doi: 10.1021/ct5002076. Epub 2014 May 9. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014. PMID: 25061447 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for targeted DNA cytosine deamination and mutagenesis by APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Feb;24(2):131-139. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3344. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27991903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anfinsen C.B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973;181:223–230. - PubMed
-
- Kauzmann W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv. Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. - PubMed
-
- Collins K.D., Washabaugh M.W. The Hofmeister effect and the behavior of water at interfaces. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1985;18:323–422. - PubMed
-
- Hofmeister F. To gauge the effect of salts [Zur lehre von der wirkung der salze] Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1888;24:247–260.
-
- Collet O. How does the first water shell fold proteins so fast? J. Chem. Phys. 2011;134:085107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

