Whole-genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation
- PMID: 23260136
- PMCID: PMC3712641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.019
Whole-genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation
Abstract
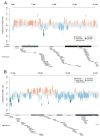
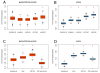
De novo mutation plays an important role in autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Notably, pathogenic copy number variants (CNVs) are characterized by high mutation rates. We hypothesize that hypermutability is a property of ASD genes and may also include nucleotide-substitution hot spots. We investigated global patterns of germline mutation by whole-genome sequencing of monozygotic twins concordant for ASD and their parents. Mutation rates varied widely throughout the genome (by 100-fold) and could be explained by intrinsic characteristics of DNA sequence and chromatin structure. Dense clusters of mutations within individual genomes were attributable to compound mutation or gene conversion. Hypermutability was a characteristic of genes involved in ASD and other diseases. In addition, genes impacted by mutations in this study were associated with ASD in independent exome-sequencing data sets. Our findings suggest that regional hypermutation is a significant factor shaping patterns of genetic variation and disease risk in humans.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Loaded dice for human genome mutation.Cell. 2012 Dec 21;151(7):1399-400. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.002. Cell. 2012. PMID: 23260131
References
-
- Amiel J, Rio M, de Pontual L, Redon R, Malan V, Boddaert N, Plouin P, Carter NP, Lyonnet S, Munnich A, et al. Mutations in TCF4, encoding a class I basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, are responsible for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a severe epileptic encephalopathy associated with autonomic dysfunction. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80:988–993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berkel S, Marshall CR, Weiss B, Howe J, Roeth R, Moog U, Endris V, Roberts W, Szatmari P, Pinto D, et al. Mutations in the SHANK2 synaptic scaffolding gene in autism spectrum disorder and mental retardation. Nat Genet. 2010;42:489–491. - PubMed
-
- Chen JM, Cooper DN, Chuzhanova N, Ferec C, Patrinos GP. Gene conversion: mechanisms, evolution and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:762–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

