Mutations in ECEL1 cause distal arthrogryposis type 5D
- PMID: 23261301
- PMCID: PMC3542461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.11.014
Mutations in ECEL1 cause distal arthrogryposis type 5D
Abstract
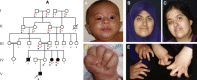
Distal arthrogryposis (DA) syndromes are the most common of the heritable congenital-contracture disorders, and ~50% of cases are caused by mutations in genes that encode contractile proteins of skeletal myofibers. DA type 5D (DA5D) is a rare, autosomal-recessive DA previously defined by us and is characterized by congenital contractures of the hands and feet, along with distinctive facial features, including ptosis. We used linkage analysis and whole-genome sequencing of a multiplex consanguineous family to identify in endothelin-converting enzyme-like 1 (ECEL1) mutations that result in DA5D. Evaluation of a total of seven families affected by DA5D revealed in five families ECEL1 mutations that explain ~70% of cases overall. ECEL1 encodes a neuronal endopeptidase and is expressed in the brain and peripheral nerves. Mice deficient in Ecel1 exhibit perturbed terminal branching of motor neurons to the endplate of skeletal muscles, resulting in poor formation of the neuromuscular junction. Our results distinguish a second developmental pathway that causes congenital-contracture syndromes.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The neuronal endopeptidase ECEL1 is associated with a distinct form of recessive distal arthrogryposis.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Apr 15;22(8):1483-92. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds514. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23236030
-
The Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations of ECEL1 Identified in a Family with Distal Arthrogryposis Type 5D.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 23;2020:2149342. doi: 10.1155/2020/2149342. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32566668 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of three novel ECEL1 mutations in three families with distal arthrogryposis type 5D.Clin Genet. 2014 Jun;85(6):568-72. doi: 10.1111/cge.12226. Epub 2013 Jul 28. Clin Genet. 2014. PMID: 23829171
-
Distal arthrogryposis type 5D in a South Indian family caused by novel deletion in ECEL1 gene.Clin Dysmorphol. 2021 Apr 1;30(2):100-103. doi: 10.1097/MCD.0000000000000364. Clin Dysmorphol. 2021. PMID: 33491998 Review.
-
New Insights of a Neuronal Peptidase DINE/ECEL1: Nerve Development, Nerve Regeneration and Neurogenic Pathogenesis.Neurochem Res. 2019 Jun;44(6):1279-1288. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2665-x. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30357652 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of ECEL1-related congenital contracture syndromes.Clin Genet. 2014 Jun;85(6):562-7. doi: 10.1111/cge.12224. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Clin Genet. 2014. PMID: 23808592 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis revealed the molecular mechanism underlying RBM10-mediated splicing regulation.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Sep;5(9):1431-42. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302663. Epub 2013 Aug 22. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24000153 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation sequencing in a large cohort of patients presenting with neuromuscular disease before or at birth.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Nov 17;10:148. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0364-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 26578207 Free PMC article.
-
Recessive variants in COL25A1 gene as novel cause of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita with ocular congenital cranial dysinnervation disorder.Hum Mutat. 2022 Apr;43(4):487-498. doi: 10.1002/humu.24333. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 35077597 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms That Contribute to Bone Marrow Pain.Front Neurol. 2017 Sep 11;8:458. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00458. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28955292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bamshad M., Jorde L.B., Carey J.C. A revised and extended classification of the distal arthrogryposes. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996;65:277–281. - PubMed
-
- Toydemir R.M., Rutherford A., Whitby F.G., Jorde L.B., Carey J.C., Bamshad M.J. Mutations in embryonic myosin heavy chain (MYH3) cause Freeman-Sheldon syndrome and Sheldon-Hall syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:561–565. - PubMed
-
- Toydemir R.M., Chen H., Proud V.K., Martin R., van Bokhoven H., Hamel B.C., Tuerlings J.H., Stratakis C.A., Jorde L.B., Bamshad M.J. Trismus-pseudocamptodactyly syndrome is caused by recurrent mutation of MYH8. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2006;140:2387–2393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HG004316/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HG004316/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN27500503415C/PHS HHS/United States
- 1RC2HG005608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG004316/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD057331/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD048895/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700023C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

