Cardiac phenotype of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: insights from cellular studies
- PMID: 23261966
- PMCID: PMC3615054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.12.009
Cardiac phenotype of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: insights from cellular studies
Abstract
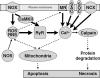
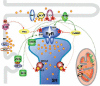
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a serious and almost inevitable complication of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, a devastating and fatal disease of skeletal muscle resulting from the lack of functional dystrophin, a protein linking the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. Ultimately, it leads to congestive heart failure and arrhythmias resulting from both cardiac muscle fibrosis and impaired function of the remaining cardiomyocytes. Here we summarize findings obtained in several laboratories, focusing on cellular mechanisms that result in degradation of cardiac functions in dystrophy.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Clarac F, Massion J, Smith AM. Duchenne, Charcot and Babinski, three neurologists of La Salpetrière Hospital, and their contribution to concepts of the central organization of motor synergy. J Physiol Paris. 2009;103:361–76. - PubMed
-
- Finsterer J, Stöllberger C. The heart in human dystrophinopathies. Cardiology. 2003;99:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Hermans MCE, Pinto YM, Merkies ISJ, de Die-Smulders CEM, Crijns HJGM, Faber CG. Hereditary muscular dystrophies and the heart. Neuromuscul Disord. 2010;20:479–92. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz A, Sechtem U. Cardiac involvement in muscular dystrophy: advances in diagnosis and therapy. Heart. 2012;98:420–9. - PubMed
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Van Deutekom JCT, Fokkema IF, Van Ommen G-JB, Dunnen Den JT. Entries in the Leiden Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutation database: An overview of mutation types and paradoxical cases that confirm the reading-frame rule. Muscle Nerve. 2006;34:135–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

