Interleukin-17 causes Rho-kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction and hypertension
- PMID: 23263331
- PMCID: PMC3583258
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvs422
Interleukin-17 causes Rho-kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction and hypertension
Abstract
Aims: Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-17A (IL-17) are associated with hypertensive autoimmune diseases; however, the connection between IL-17 and hypertension is unknown. We hypothesized that IL-17 increases blood pressure by decreasing endothelial nitric oxide production.
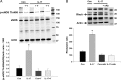
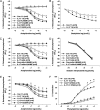
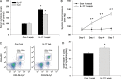
Methods and results: Acute treatment of endothelial cells with IL-17 caused a significant increase in phosphorylation of the inhibitory endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase residue threonine 495 (eNOS Thr495). Of the kinases known to phosphorylate eNOS Thr495, only inhibition of Rho-kinase prevented the IL-17-induced increase. IL-17 caused a threefold increase in the Rho-kinase activator RhoA, and this was prevented by an IL-17 neutralizing antibody. In isolated mouse aortas, IL-17 significantly increased eNOS Thr495 phosphorylation, induced RhoA expression, and decreased NO-dependent relaxation responses, all of which were prevented by either an IL-17 neutralizing antibody or inhibition of Rho-kinase. In mice, IL-17 treatment for 1 week significantly increased systolic blood pressure and this was associated with decreased aortic NO-dependent relaxation responses, increased eNOS Thr495 phosphorylation, and increased RhoA expression. Inhibition of Rho-kinase prevented the hypertension caused by IL-17.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that IL-17 activates RhoA/Rho-kinase leading to endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Inhibitors of IL-17 or Rho-kinase may prove useful as anti-hypertensive drugs in IL-17-associated autoimmune diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Gaffen SL. An overview of IL-17 function and signaling. Cytokine. 2008;43:402–407. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaffen SL, Kramer JM, Yu JJ, Shen F. The IL-17 cytokine family. Vitam Horm. 2006;74:255–282. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(06)74010-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Onishi RM, Gaffen SL. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology. 2010;129:311–321. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03240.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL, Miossec P. Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 1998;161:409–414. - PubMed
-
- Hata K, Andoh A, Shimada M, Fujino S, Bamba S, Araki Y, et al. IL-17 stimulates inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways in human colonic myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;282:G1035–G1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

