An endothelial apelin-FGF link mediated by miR-424 and miR-503 is disrupted in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 23263626
- PMCID: PMC3540168
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3040
An endothelial apelin-FGF link mediated by miR-424 and miR-503 is disrupted in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
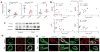
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is characterized by vascular remodeling associated with obliteration of pulmonary arterioles and formation of plexiform lesions composed of hyperproliferative endothelial and vascular smooth-muscle cells. Here we describe a microRNA (miRNA)-dependent association between apelin (APLN) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) signaling in pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs). APLN deficiency in these cells led to increased expression of FGF2 and its receptor FGFR1 as a consequence of decreased expression of miR-424 and miR-503, which directly target FGF2 and FGFR1. miR-424 and miR-503 were downregulated in PAH, exerted antiproliferative effects in PAECs and inhibited the capacity of PAEC-conditioned medium to induce the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth-muscle cells. Reconstitution of miR-424 and miR-503 in vivo ameliorated pulmonary hypertension in experimental models. These studies identify an APLN-dependent miRNA-FGF signaling axis needed for the maintenance of pulmonary vascular homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

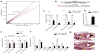
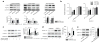


Comment in
-
High-frequency oscillatory ventilation, microRNAs in pulmonary hypertension, and gastric residual volumes.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Aug 15;188(4):508-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201304-0672RR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23947518 No abstract available.
-
Unanticipated role of apelin: regulation of miRNA generation.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013 Oct;45(10):896-8. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt090. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013. PMID: 23985306 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- HL095654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL093362/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 HL069170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HL101284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL093362/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL113005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL095654/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL060917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL101284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL069170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

