Adenylyl cyclase VI mediates vasopressin-stimulated ENaC activity
- PMID: 23264685
- PMCID: PMC3559481
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012050449
Adenylyl cyclase VI mediates vasopressin-stimulated ENaC activity
Abstract
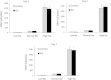
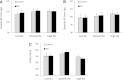
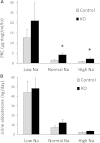
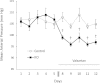
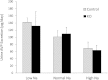
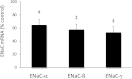
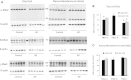
Vasopressin modulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct through adenylyl cyclase-stimulated cyclic AMP, which exists as multiple isoforms; the specific isoform involved in vasopressin-stimulated sodium transport is unknown. To assess this, we studied mice deficient in adenylyl cyclase type VI specifically in the principal cells of the collecting duct. Knockout mice had increased urine volume and reduced urine sodium concentration, but regardless of the level of sodium intake, they did not exhibit significant alterations in urinary sodium excretion, arterial pressure, or pulse rate. Plasma renin concentration was elevated in knockout mice, however, suggesting a compensatory response. Valsartan significantly reduced arterial pressure in knockout mice but not in controls. Knockout mice had decreased renal cortical mRNA content of all three epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) isoforms, and total cell sodium channel isoforms α and γ were reduced in these animals. Patch-clamp analysis of split-open cortical collecting ducts revealed no difference in baseline activity of sodium channels, but knockout mice had abolished vasopressin-stimulated ENaC open probability and apical membrane channel number. In summary, these data suggest that adenylyl cyclase VI mediates vasopressin-stimulated ENaC activity in the kidney.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of the epithelial Na+ channel in the collecting duct by vasopressin contributes to water reabsorption.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Nov;297(5):F1411-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00371.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19692483 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of an effect of collecting duct-specific deletion of adenylyl cyclase 3 on renal Na+ and water excretion or arterial pressure.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Mar 15;306(6):F597-607. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00505.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24431204 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3beta mediates renal response to vasopressin by modulating adenylate cyclase activity.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Mar;21(3):428-37. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060672. Epub 2010 Jan 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20056751 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin is required for vasopressin-stimulated increase in cyclic AMP production in inner medullary collecting duct.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 8;280(14):13624-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500040200. Epub 2005 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15710610 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated Control of ENaC and Na+,K+-ATPase in Renal Collecting Duct.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Sep;27(9):2554-63. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016020124. Epub 2016 May 17. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27188842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Net K+ secretion in the thick ascending limb of mice on a low-Na, high-K diet.Kidney Int. 2017 Oct;92(4):864-875. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28688582 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 stimulates the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in cultured mouse cortical collecting duct cells in an autocrine manner.J Gen Physiol. 2020 Aug 3;152(8):e201912525. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912525. J Gen Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32442241 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel in Renal Principal Cells by Gs-Coupled Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 25;12:725782. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.725782. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34512393 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Endothelin system during the postnatal nephrogenic period in the rat. Its relationship with hypertension and renal disease in adulthood.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 3;15(3):e0229756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229756. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32126132 Free PMC article.
-
Role of α2-Adrenoceptors in Hypertension: Focus on Renal Sympathetic Neurotransmitter Release, Inflammation, and Sodium Homeostasis.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 9;11:566871. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.566871. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33240096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stockand JD: Vasopressin regulation of renal sodium excretion. Kidney Int 78: 849–856, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Ecelbarger CA, Kim GH, Terris J, Masilamani S, Mitchell C, Reyes I, Verbalis JG, Knepper MA: Vasopressin-mediated regulation of epithelial sodium channel abundance in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279: F46–F53, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Lahr TF, Record RD, Hoover DK, Hughes CL, Blazer-Yost BL: Characterization of the ion transport responses to ADH in the MDCK-C7 cell line. Pflugers Arch 439: 610–617, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Schafer J, Williams J Jr: Flux measurements in isolated perfused tubules. In: Methods in Enzymology, edited by Fleischer SFB, San Diego, CA, Academic Press, 1990, pp 354–370 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

