Cubilin and amnionless mediate protein reabsorption in Drosophila nephrocytes
- PMID: 23264686
- PMCID: PMC3559489
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012080795
Cubilin and amnionless mediate protein reabsorption in Drosophila nephrocytes
Abstract
The insect nephrocyte and the mammalian glomerular podocyte are similar with regard to filtration, but it remains unclear whether there is an organ or cell type in flies that reabsorbs proteins. Here, we show that the Drosophila nephrocyte has molecular, structural, and functional similarities to the renal proximal tubule cell. We screened for genes required for nephrocyte function and identified two Drosophila genes encoding orthologs of mammalian cubilin and amnionless (AMN), two major receptors for protein reabsorption in the proximal tubule. In Drosophila, expression of dCubilin and dAMN is specific to nephrocytes, where they function as co-receptors for protein uptake. Targeted expression of human AMN in Drosophila nephrocytes was sufficient to rescue defective protein uptake induced by dAMN knockdown, suggesting evolutionary conservation of Cubilin/AMN co-receptors function from flies to humans. Furthermore, we found that Cubilin/AMN-mediated protein reabsorption is required for the maintenance of nephrocyte ultrastructure and fly survival under conditions of toxic stress. In conclusion, the insect nephrocyte combines filtration with protein reabsorption, using evolutionarily conserved genes and subcellular structures, suggesting that it can serve as a simplified model for both podocytes and the renal proximal tubule.
Figures
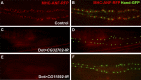


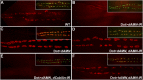
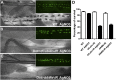
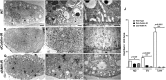
Comment in
-
The Drosophila nephrocyte: back on stage.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Feb;24(2):161-3. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012121227. Epub 2013 Jan 18. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23334393 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pavenstädt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M: Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev 83: 253–307, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Christensen EI, Verroust PJ, Nielsen R: Receptor-mediated endocytosis in renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch 458: 1039–1048, 2009 - PubMed
-
- D’Agati VD, Kaskel FJ, Falk RJ: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 365: 2398–2411, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

