HER2/neu DNA vaccination by intradermal gene delivery in a mouse tumor model: Gene gun is superior to jet injector in inducing CTL responses and protective immunity
- PMID: 23264900
- PMCID: PMC3525609
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.22563
HER2/neu DNA vaccination by intradermal gene delivery in a mouse tumor model: Gene gun is superior to jet injector in inducing CTL responses and protective immunity
Abstract
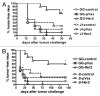
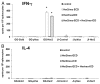
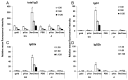
DNA vaccines are potential tools for the induction of immune responses against both infectious disease and cancer. The dermal application of DNA vaccines is of particular interest since the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin are characterized by an abundance of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The aim of our study was to compare tumor protection as obtained by two different methods of intradermal DNA delivery (gene gun and jet injector) in a well-established HER2/neu mouse tumor model. BALB/c mice were immunized twice with a HER2/neu-coding plasmid by gene gun or jet injector. Mice were then subcutaneously challenged with HER2/neu(+) syngeneic D2F2/E2 tumor cells. Protection against subsequent challenges with tumor cells as well as humoral and T-cell immune responses induced by the vaccine were monitored. Gene gun immunization was far superior to jet injector both in terms of tumor protection and induction of HER2/neu-specific immune responses. After gene gun immunization, 60% of the mice remained tumor-free until day 140 as compared with 25% after jet injector immunization. Furthermore, gene gun vaccination was able to induce both a strong T(H)1-polarized T-cell response with detectable cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity and a humoral immune response against HER2/neu, whereas the jet injector was not. Although the disadvantages that were associated with the use of the jet injector in our model may be overcome with methodological modifications and/or in larger animals, which exhibit a thicker skin and/or subcutaneous muscle tissue, we conclude that gene gun delivery constitutes the method of choice for intradermal DNA delivery in preclinical mouse models and possibly also for the clinical development of DNA-based vaccines.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
