Successful expression and purification of DPPD using a codon optimized synthetic gene
- PMID: 23264930
- PMCID: PMC3527103
- DOI: 10.4236/oji.2011.11001
Successful expression and purification of DPPD using a codon optimized synthetic gene
Abstract
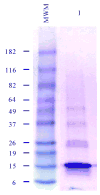
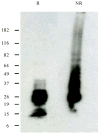
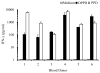
DPPD (Rv0061) is a difficult to express protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that elicits strong and specific delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in humans infected with M. tuberculosis. Therefore e DPPD is a molecule that can improve the specificity of the tuberculin skin test, which is widely used as an aid for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. However, a pitfall of our initial studies was that the DPPD molecule used to perform the skin tests was engineered as fusion molecule with another Mycobacterium protein. This approach was used because no expression of DPPD could be achieved either as a single molecule or as a fusion protein using a variety of commercially available expression systems. Here, we report the production and purification of rDPPD using a synthetic gene engineered to contain E. coli codon bias. The gene was cloned into pET14b expression vector, which was subsequently used to transform Rosetta 2(DE3) pLysS or BL-21(DE3)pLysS host cells. The recombinant protein was over-expressed after induction with IPTG and its purification was easily achieved at levels of 5 - 10 mg/l of bacterial broth cultures. The purified protein was confirmed to be DPPD by Mass Spectroscopy sequencing analysis. Moreover, purified rDPPD stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells of PPD positive blood donors to produce high levels of IFN-γ, thus confirming that this molecule is biologically active. Because of the DPPD gene is restricted to the tuberculosis-complex organisms of Mycobacterium genus, this highly purified molecule should be useful for the identification of individuals sensitized with tubercle bacilli.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any financial conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and purification of immunologically reactive DPPD, a recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis skin test antigen, using Mycobacterium smegmatis and Escherichia coli host cells.Can J Microbiol. 2004 Feb;50(2):97-105. doi: 10.1139/w03-109. Can J Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15052311
-
Evaluation of DPPD, a single recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein as an alternative antigen for the Mantoux test.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2001;81(5-6):353-8. doi: 10.1054/tube.2001.0311. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2001. PMID: 11800586 Clinical Trial.
-
Cloning of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene encoding a purifed protein derivative protein that elicits strong tuberculosis-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity.J Infect Dis. 2000 Jul;182(1):224-33. doi: 10.1086/315677. Epub 2000 Jul 6. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10882601
-
[Evolution of IGRA researches].Kekkaku. 2008 Sep;83(9):641-52. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18979999 Review. Japanese.
-
Bovine tuberculosis: effect of the tuberculin skin test on in vitro interferon gamma responses.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Jul;136(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20219253 Review.
References
-
- Coler RN, Skeiky YA, Ovendale PJ, Vedvick TS, Gervassi L, Guderian J, Jen S, Reed SG, Campos-Neto A. Cloning of a gene encoding a purified protein derivative protein that elicits strong tuberculosis-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2000;182:224–233. doi: 10.1086/315677. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schiller I, Vordermeier HM, Waters WR, Whelan AO, Coad M, Gormley E, Buddle BM, Palmer M, Thacker T, McNair J, Welsh M, Hewinson RG, Oesch B. Bovine tuberculosis: Effect of the tuberculin skin test on in vitro interferon gamma responses. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology. 2010;136:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
