Simultaneous Determination of Atorvastatin and Aspirin in Human Plasma by LC-MS/MS: Its Pharmacokinetic Application
- PMID: 23264940
- PMCID: PMC3528047
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1206-12
Simultaneous Determination of Atorvastatin and Aspirin in Human Plasma by LC-MS/MS: Its Pharmacokinetic Application
Abstract
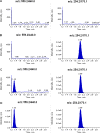
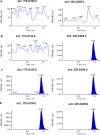
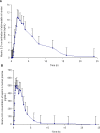
A simple, rapid, and sensitive liquid chromatography tandem mass spectro-metric (LC-MS/MS) assay method has been developed and fully validated for the simultaneous quantification of atorvastatin and aspirin in human plasma using a polarity switch. Proguanil and furosemide were used as the internal standards for the quantification of atorvastatin and aspirin, respectively. The analytes were extracted from human plasma by the liquid-liquid extraction technique using methyl tert-butyl ether. The reconstituted samples were chromatographed on a Zorbax XDB Phenyl column by using a mixture of 0.2% acetic acid buffer, methanol, and acetonitrile (20:16:64, v/v) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min. Prior to detection, atorvastatin and aspirin were ionized using an ESI source in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. The ions were monitored at the positive m/z 559.2→440.0 transition for atorvastatin and the negative m/z 179.0→136.6 transition for aspirin. The calibration curve obtained was linear (r(2) ≥ 0.99) over the concentration range of 0.20-151 ng/mL for atorvastatin and 15.0-3000 ng/mL for aspirin. The method validation was performed as per FDA guidelines and the results met the acceptance criteria. A run time of 3.0 min for each sample made it possible to analyze more than 300 human plasma samples per day. The proposed method was found to be applicable to clinical studies.
Keywords: Acetylsalicylic acid; Aspirin; Atorvastatin; Chromatography; Liquid–liquid extraction; Pharmacokinetics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometric method for the simultaneous quantification of pravastatin and aspirin in human plasma: Pharmacokinetic application.J Pharm Anal. 2012 Jun;2(3):206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Feb 4. J Pharm Anal. 2012. PMID: 29403744 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous determination of atorvastatin, metformin and glimepiride in human plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a human pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Anal. 2013 Feb;3(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Oct 3. J Pharm Anal. 2013. PMID: 29403791 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous determination of telmisartan and amlodipine in human plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application in a human pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Anal. 2012 Oct;2(5):319-326. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Apr 4. J Pharm Anal. 2012. PMID: 29403761 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous determination of carisoprodol and aspirin in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in polarity switch mode: application to a human pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2013 Feb;27(2):179-85. doi: 10.1002/bmc.2766. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Biomed Chromatogr. 2013. PMID: 22674769
-
Simultaneous quantification of lidocaine and prilocaine in human plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application in a human pharmacokinetic study.Pract Lab Med. 2019 Jul 30;17:e00129. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2019.e00129. eCollection 2019 Nov. Pract Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31414038 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ecofriendly first-derivative synchronous fluorometric method for simultaneous determination of atorvastatin and aspirin in pharmaceutical preparations.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17787. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99718-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404853 Free PMC article.
-
Depot injectable atorvastatin biodegradable in situ gel: development, optimization, in vitro, and in vivo evaluation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Jan 20;10:405-15. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S98078. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26855565 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin inhibits cell viability and mTOR downstream signaling in gastroenteropancreatic and bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumor cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 7;20(29):10038-49. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25110431 Free PMC article.
-
Based on Multi-Activity Integrated Strategy to Screening, Characterization and Quantification of Bioactive Compounds from Red Wine.Molecules. 2021 Nov 8;26(21):6750. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216750. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain KS, Kathiravan MK, Somani RS, Shishoo CJ. The biology and chemistry of hyperlipedemia. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:4674–4699. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2007.04.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB. Risk stratification in hypertension: new insights from the Famingham Study. Am J Hypertens. 2000;1:3S–10S. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(99)00252-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davidson MH, Toth PP. Comparative effects of lipid–lowering therapies. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2004;47:73–104. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2004.04.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corsini A, Bellosta S, Baetta R, Fumagalli R, Paoletti R, Bernini F. New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacol Ther. 1999;84:413–428. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0163-7258(99)00045-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bakker–Arkema RG, Davidson MH, Goldstein RJ, Davignon RJ, Isaacsohn SL, Weiss SR, Keilson LM, Brown MV, Miller VT, Shurzinske LJ. Efficiency and safety of a new HMG–CoA reductase inhibitor atorvastatin in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA. 1996;275:128–133. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.1996.03530260042029. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
