OmpR, a response regulator of the two-component signal transduction pathway, influences inv gene expression in Yersinia enterocolitica O9
- PMID: 23264953
- PMCID: PMC3524506
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00153
OmpR, a response regulator of the two-component signal transduction pathway, influences inv gene expression in Yersinia enterocolitica O9
Abstract
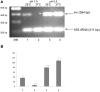
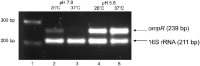
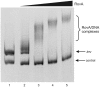
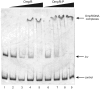
The environmental control of invasin (inv) expression in Yersinia enterocolitica is mediated by a regulatory network composed of negative and positive regulators of inv gene transcription. Previously, we demonstrated that OmpR, a response regulator of the two-component signal transduction pathway EnvZ/OmpR, negatively regulates inv gene expression in Y. enterocolitica O9 by direct interaction with the inv promoter region. This study was undertaken to clarify the role of OmpR in the inv regulatory circuit in which RovA protein has been shown to positively regulate inv transcription. Using ompR, rovA, and ompR rovA Y. enterocolitica mutant backgrounds we showed that the inhibitory effect of OmpR on inv transcription may be observed only when RovA is present/active in Y. enterocolitica cells. To extend our research on inv regulation we examined the effect of OmpR on rovA gene expression. Analysis of rovA-lacZ transcriptional fusion in Y. enterocolitica wild-type and ompR background indicated that OmpR does not influence rovA expression. Thus, our results indicate that OmpR influences inv expression directly via binding to the inv promoter, but not through modulation of rovA expression.
Keywords: OmpR regulator; RovA regulator; Yersinia enterocolitica; invasin; signal transduction pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
OmpR negatively regulates expression of invasin in Yersinia enterocolitica.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Aug;153(Pt 8):2416-2425. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/003202-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17660406
-
Modulation of inv gene expression by the OmpR two-component response regulator protein of Yersinia enterocolitica.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011 Jul;56(4):313-9. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0054-9. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011. PMID: 21818612
-
H-NS represses inv transcription in Yersinia enterocolitica through competition with RovA and interaction with YmoA.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(14):5101-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00862-05. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16816182 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory elements implicated in the environmental control of invasin expression in enteropathogenic Yersinia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:156-66. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966412 Review.
-
Invasin and beyond: regulation of Yersinia virulence by RovA.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Jun;12(6):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.04.006. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15165608 Review.
Cited by
-
OmpR-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation and Function of Two Heme Receptor Proteins of Yersinia enterocolitica Bio-Serotype 2/O:9.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Sep 20;8:333. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00333. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30294593 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of host and endosymbiont gene expression governs endosymbiont growth and elimination in the cereal weevil Sitophilus spp.Microbiome. 2023 Dec 13;11(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01714-8. Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 38087390 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of two-component regulatory systems in antibiotic resistance.Future Microbiol. 2019 Apr;14(6):533-552. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2019-0002. Epub 2019 May 8. Future Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31066586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of the AcrAB Components of the AcrAB-TolC Multidrug Efflux Pump of Yersinia enterocolitica Is Subject to Dual Regulation by OmpR.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 20;10(4):e0124248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124248. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25893523 Free PMC article.
-
Human Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infection via bath water - case report and genome announcement.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 24;12:981477. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.981477. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36353709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiba H., Nakasai F., Mizushima S., Mizuno T. (1989). Evidence for the physiological importance of the phosphotransfer between the two regulatory components, EnvZ and OmpR, in osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 14090–14094 - PubMed
-
- Baumler A. J., Tsolis R. M., van der Velden A. W. M., Stojiljkovic I., Anic S., Heffron F. (1996). Identification of a new iron regulated locus of Salmonella typhi. Gene 183, 207–213 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

