Streamlined expressed protein ligation using split inteins
- PMID: 23265282
- PMCID: PMC3544275
- DOI: 10.1021/ja309126m
Streamlined expressed protein ligation using split inteins
Abstract
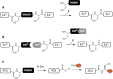
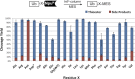
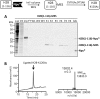
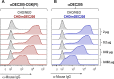
Chemically modified proteins are invaluable tools for studying the molecular details of biological processes, and they also hold great potential as new therapeutic agents. Several methods have been developed for the site-specific modification of proteins, one of the most widely used being expressed protein ligation (EPL) in which a recombinant α-thioester is ligated to an N-terminal Cys-containing peptide. Despite the widespread use of EPL, the generation and isolation of the required recombinant protein α-thioesters remain challenging. We describe here a new method for the preparation and purification of recombinant protein α-thioesters using engineered versions of naturally split DnaE inteins. This family of autoprocessing enzymes is closely related to the inteins currently used for protein α-thioester generation, but they feature faster kinetics and are split into two inactive polypeptides that need to associate to become active. Taking advantage of the strong affinity between the two split intein fragments, we devised a streamlined procedure for the purification and generation of protein α-thioesters from cell lysates and applied this strategy for the semisynthesis of a variety of proteins including an acetylated histone and a site-specifically modified monoclonal antibody.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Split-inteins and their bioapplications.Biotechnol Lett. 2015 Nov;37(11):2121-37. doi: 10.1007/s10529-015-1905-2. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Biotechnol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26153348 Review.
-
Ultrafast protein splicing is common among cyanobacterial split inteins: implications for protein engineering.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Jul 18;134(28):11338-41. doi: 10.1021/ja303226x. Epub 2012 Jul 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22734434 Free PMC article.
-
Semisynthesis of proteins using split inteins.Methods Enzymol. 2009;462:77-96. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)62004-8. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19632470
-
Protein derivitization-expressed protein ligation.Methods Enzymol. 2014;536:95-108. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420070-8.00009-X. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 24423270
-
Biotechnological Applications of Protein Splicing.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(5):408-424. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666190208110416. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 30734675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Generating RNA Exosome Complexes from Recombinant Expression Hosts.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2062:417-425. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9822-7_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31768988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Histone Labeling Using Ultrafast trans-Splicing Inteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2133:201-219. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0434-2_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32144669 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical modifications of proteins and their applications in metalloenzyme studies.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2021 Feb 15;6(1):32-49. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2021.01.001. eCollection 2021 Mar. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33665390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Antibody-Antibiotic Conjugates to Fight Bacterial Infections.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 7;13:835677. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.835677. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35330773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Evolution of Intein-Based Affinity Methods as Reflected in 30 years of Patent History.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 8;9:857566. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.857566. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35463948 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stephanopoulos N.; Francis M. B. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 876–84. - PubMed
-
- Carter P. J. Exp. Cell. Res. 2011, 317, 1261–9. - PubMed
-
- Kent S. B. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 338–51. - PubMed
-
- Liu C. C.; Schultz P. G. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 413–444. - PubMed
-
- Hackenberger C. P. R.; Schwarzer D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 10030–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

