The pseudopeptide HB-19 binds to cell surface nucleolin and inhibits angiogenesis
- PMID: 23265284
- PMCID: PMC3606460
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-824X-4-21
The pseudopeptide HB-19 binds to cell surface nucleolin and inhibits angiogenesis
Abstract
Background: Nucleolin is a protein over-expressed on the surface of tumor and endothelial cells. Recent studies have underlined the involvement of cell surface nucleolin in tumor growth and angiogenesis. This cell surface molecule serves as a receptor for various ligands implicated in pathophysiological processes such as growth factors, cell adhesion molecules like integrins, selectins or laminin-1, lipoproteins and viruses (HIV and coxsackie B). HB-19 is a synthetic multimeric pseudopeptide that binds cell surface expressed nucleolin and inhibits both tumor growth and angiogenesis.
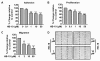
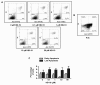
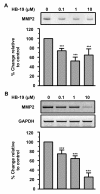
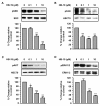
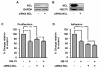
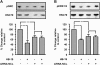
Methodology/principal findings: In the present work, we further investigated the biological actions of pseudopeptide HB-19 on HUVECs. In a previous work, we have shown that HB-19 inhibits the in vivo angiogenesis on the chicken embryo CAM assay. We now provide evidence that HB-19 inhibits the in vitro adhesion, migration and proliferation of HUVECs without inducing their apoptosis. The above biological actions seem to be regulated by SRC, ERK1/2, AKT and FAK kinases as we found that HB-19 inhibits their activation in HUVECs. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play crucial roles in tumor growth and angiogenesis, so we investigated the effect of HB-19 on the expression of MMP-2 and we found that HB-19 downregulates MMP-2 in HUVECs. Finally, down regulation of nucleolin using siRNA confirmed the implication of nucleolin in the biological actions of these peptides.
Conclusions/significance: Taken together, these results indicate that HB-19 could constitute an interesting tool for tumor therapy strategy, targeting cell surface nucleolin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nucleolin mediates the antiangiogenesis effect of the pseudopeptide N6L.BMC Cell Biol. 2012 Nov 13;13:32. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-13-32. BMC Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23146273 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of tumor growth and angiogenesis by a specific antagonist of the cell-surface expressed nucleolin.PLoS One. 2008 Jun 18;3(6):e2518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002518. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18560571 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting surface nucleolin with multivalent HB-19 and related Nucant pseudopeptides results in distinct inhibitory mechanisms depending on the malignant tumor cell type.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 3;11:333. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-333. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21812966 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-HIV pseudopeptide HB-19 forms a complex with the cell-surface-expressed nucleolin independent of heparan sulfate proteoglycans.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 24;274(39):27875-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27875. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10488134
-
Midkine, a cytokine that inhibits HIV infection by binding to the cell surface expressed nucleolin.Cell Res. 2006 Feb;16(2):174-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310024. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16474431 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel nucleolin-binding peptide for Cancer Theranostics.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 14;10(20):9153-9171. doi: 10.7150/thno.43502. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32802184 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue and cellular characterisation of nucleolin in a murine model of corneal angiogenesis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Sep;254(9):1753-63. doi: 10.1007/s00417-016-3409-8. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27313162
-
Human anti-nucleolin recombinant immunoagent for cancer therapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 28;112(30):9418-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507087112. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26170308 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Factor Midkine Aggravates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension via Surface Nucleolin.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 25;10(1):10345. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67217-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32587339 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin‑based targeting strategies in cancer treatment: Focus on cancer immunotherapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Sep;52(3):81. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5284. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37477132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srivastava M, Pollard HB. Molecular dissection of nucleolin’s role in growth and cell proliferation: new insights. FASEB J. 1999;13:1911–1922. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

