Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in overnutrition-induced diseases
- PMID: 23265946
- PMCID: PMC3556486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.11.003
Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in overnutrition-induced diseases
Abstract
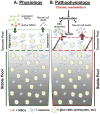
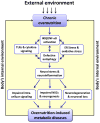
Overnutrition-induced diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) involve neural dysregulation of metabolic physiology. Recently, interdisciplinary research in neuroscience and immunology has linked overnutrition to a non-classical onset of inflammation in the brain, particularly in the hypothalamus. This neuroinflammation impairs central regulatory pathways of energy balance and nutrient metabolism, and leads to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular complications. This review describes recent findings on the roles of overnutrition-induced hypothalamic inflammation in neurodegeneration and defective adult neurogenesis, as well as in impaired neural stem cell regeneration, and their relevance to obesity and related diseases. In addition, commonalities in terms of neuroinflammation between neurodegenerative diseases and overnutrition-induced metabolic diseases are discussed. Targeting neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration will provide promising approaches for treating obesity and other overnutrition-related diseases.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Belgardt BF, Bruning JC. CNS leptin and insulin action in the control of energy homeostasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1212:97–113. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG, et al. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:537–556. - PubMed
-
- Elmquist JK, Flier JS. Neuroscience. The fat-brain axis enters a new dimension. Science. 2004;304:63–64. - PubMed
-
- Rahmouni K, et al. Obesity-associated hypertension: new insights into mechanisms. Hypertension. 2005;45:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

