Caenorhabditis elegans PIG-1/MELK acts in a conserved PAR-4/LKB1 polarity pathway to promote asymmetric neuroblast divisions
- PMID: 23267054
- PMCID: PMC3584005
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.112.148106
Caenorhabditis elegans PIG-1/MELK acts in a conserved PAR-4/LKB1 polarity pathway to promote asymmetric neuroblast divisions
Abstract
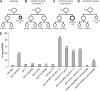
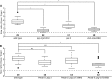
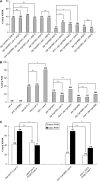
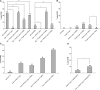
Asymmetric cell divisions produce daughter cells with distinct sizes and fates, a process important for generating cell diversity during development. Many Caenorhabditis elegans neuroblasts, including the posterior daughter of the Q cell (Q.p), divide to produce a larger neuron or neuronal precursor and a smaller cell that dies. These size and fate asymmetries require the gene pig-1, which encodes a protein orthologous to vertebrate MELK and belongs to the AMPK-related family of kinases. Members of this family can be phosphorylated and activated by the tumor suppressor kinase LKB1, a conserved polarity regulator of epithelial cells and neurons. In this study, we present evidence that the C. elegans orthologs of LKB1 (PAR-4) and its partners STRAD (STRD-1) and MO25 (MOP-25.2) regulate the asymmetry of the Q.p neuroblast division. We show that PAR-4 and STRD-1 act in the Q lineage and function genetically in the same pathway as PIG-1. A conserved threonine residue (T169) in the PIG-1 activation loop is essential for PIG-1 activity, consistent with the model that PAR-4 (or another PAR-4-regulated kinase) phosphorylates and activates PIG-1. We also demonstrate that PIG-1 localizes to centrosomes during cell divisions of the Q lineage, but this localization does not depend on T169 or PAR-4. We propose that a PAR-4-STRD-1 complex stimulates PIG-1 kinase activity to promote asymmetric neuroblast divisions and the generation of daughter cells with distinct fates. Changes in cell fate may underlie many of the abnormal behaviors exhibited by cells after loss of PAR-4 or LKB1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NMY-2, TOE-2 and PIG-1 regulate Caenorhabditis elegans asymmetric cell divisions.PLoS One. 2024 May 24;19(5):e0304064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304064. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38787850 Free PMC article.
-
The C. elegans MELK ortholog PIG-1 regulates cell size asymmetry and daughter cell fate in asymmetric neuroblast divisions.Development. 2006 Jul;133(14):2747-56. doi: 10.1242/dev.02447. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Development. 2006. PMID: 16774992
-
Caenorhabditis elegans CES-1 Snail Represses pig-1 MELK Expression To Control Asymmetric Cell Division.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):2069-2084. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.202754. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28652378 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cell Polarity by PAR-1/MARK Kinase.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;123:365-397. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28236972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Par-3 family proteins in cell polarity & adhesion.FEBS J. 2022 Feb;289(3):596-613. doi: 10.1111/febs.15754. Epub 2021 Mar 3. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33565714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A caspase-RhoGEF axis contributes to the cell size threshold for apoptotic death in developing Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Biol. 2022 Oct 6;20(10):e3001786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001786. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 36201522 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 protects glioma stem cells from radiation-induced cell death in a MELK/FOXM1-dependent manner.Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Feb 10;4(2):226-38. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.12.006. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Stem Cell Reports. 2015. PMID: 25601206 Free PMC article.
-
'Biogeneric' developmental processes: drivers of major transitions in animal evolution.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Aug 19;371(1701):20150443. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0443. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27431521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical cell death in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Methods Enzymol. 2014;545:157-80. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801430-1.00007-X. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 25065890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMY-2, TOE-2 and PIG-1 regulate Caenorhabditis elegans asymmetric cell divisions.PLoS One. 2024 May 24;19(5):e0304064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304064. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38787850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baas A. F., Kuipers J., van der Wel N. N., Batlle E., Koerten H. K., et al. , 2004. Complete polarization of single intestinal epithelial cells upon activation of LKB1 by STRAD. Cell 116: 457–466. - PubMed
-
- Barnes A. P., Lilley B. N., Pan Y. A., Plummer L. J., Powell A. W., et al. , 2007. LKB1 and SAD kinases define a pathway required for the polarization of cortical neurons. Cell 129: 549–563. - PubMed
-
- Beullens M., Vancauwenbergh S., Morrice N., Derua R., Ceulemans H., et al. , 2005. Substrate specificity and activity regulation of protein kinase MELK. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 40003–40011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

