Mice with an adipocyte-specific lipin 1 separation-of-function allele reveal unexpected roles for phosphatidic acid in metabolic regulation
- PMID: 23267081
- PMCID: PMC3545773
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213493110
Mice with an adipocyte-specific lipin 1 separation-of-function allele reveal unexpected roles for phosphatidic acid in metabolic regulation
Abstract
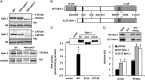
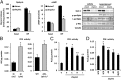
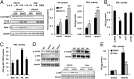
Lipin 1 is a coregulator of DNA-bound transcription factors and a phosphatidic acid (PA) phosphatase (PAP) enzyme that catalyzes a critical step in the synthesis of glycerophospholipids. Lipin 1 is highly expressed in adipocytes, and constitutive loss of lipin 1 blocks adipocyte differentiation; however, the effects of Lpin1 deficiency in differentiated adipocytes are unknown. Here we report that adipocyte-specific Lpin1 gene recombination unexpectedly resulted in expression of a truncated lipin 1 protein lacking PAP activity but retaining transcriptional regulatory function. Loss of lipin 1-mediated PAP activity in adipocytes led to reduced glyceride synthesis and increased PA content. Characterization of the deficient mice also revealed that lipin 1 normally modulates cAMP-dependent signaling through protein kinase A to control lipolysis by metabolizing PA, which is an allosteric activator of phosphodiesterase 4 and the molecular target of rapamycin. Consistent with these findings, lipin 1 expression was significantly related to adipose tissue lipolytic rates and protein kinase A signaling in adipose tissue of obese human subjects. Taken together, our findings identify lipin 1 as a reciprocal regulator of triglyceride synthesis and hydrolysis in adipocytes, and suggest that regulation of lipolysis by lipin 1 is mediated by PA-dependent modulation of phosphodiesterase 4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Fang Y, Vilella-Bach M, Bachmann R, Flanigan A, Chen J. Phosphatidic acid-mediated mitogenic activation of mTOR signaling. Science. 2001;294(5548):1942–1945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM50388/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR-21954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK37948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK037948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK78187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR021954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR024598/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM050388/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK52574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

