Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience
- PMID: 23267351
- PMCID: PMC3525951
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00417
Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience
Abstract
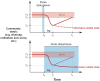
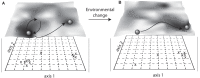
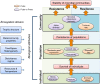
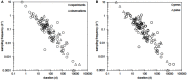
Microbial communities are at the heart of all ecosystems, and yet microbial community behavior in disturbed environments remains difficult to measure and predict. Understanding the drivers of microbial community stability, including resistance (insensitivity to disturbance) and resilience (the rate of recovery after disturbance) is important for predicting community response to disturbance. Here, we provide an overview of the concepts of stability that are relevant for microbial communities. First, we highlight insights from ecology that are useful for defining and measuring stability. To determine whether general disturbance responses exist for microbial communities, we next examine representative studies from the literature that investigated community responses to press (long-term) and pulse (short-term) disturbances in a variety of habitats. Then we discuss the biological features of individual microorganisms, of microbial populations, and of microbial communities that may govern overall community stability. We conclude with thoughts about the unique insights that systems perspectives - informed by meta-omics data - may provide about microbial community stability.
Keywords: community structure; disturbance; microbial ecology; perturbation; sensitivity; stability; structure-function; time series.
Figures


References
-
- Cleveland C. C., Nemergut D. R., Schmidt S. K., Townsend A. R. (2007). Increases in soil respiration following labile carbon additions linked to rapid shifts in soil microbial community composition. Biogeochemistry 82, 229–24010.1007/s10533-006-9065-z - DOI
-
- Allison G. (2004). The influence of species diversity and stress intensity on community resistance and resilience. Ecol. Monogr. 74, 117–13410.1890/02-0681 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

