World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow's Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guidelines
- PMID: 23268426
- PMCID: PMC3488907
- DOI: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e3181defeb9
World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow's Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guidelines
Figures



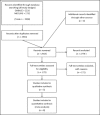
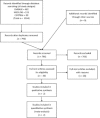









References
REFERENCES, SECTION 1
-
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. Food allergy: a practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;96(Suppl 2):S1–S68 - PubMed
-
- Mukoyama T, Nishima S, Arita M, Ito S, Urisu A, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of pediatric food allergy in Japan. Allergol Int. 2007;56:349 –361 - PubMed
-
- Prescott SL. The Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy position statement: Summary of allergy prevention in children. Med J Aust. 2005;182:464–467 - PubMed
-
- Muraro A, Dreborg S, Halken S, Høst A, Niggemann B, et al. Dietary prevention of allergic diseases in infants and small children. Part III: Critical review of published peer-reviewed observational and interventional studies and final recommendations. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004;15:291–307 - PubMed
-
- Muraro A, Dreborg S, Halken S, Høst A, Niggemann B, et al. Dietary prevention of allergic diseases in infants and small children. Part I: immunologic background and criteria for hypoallergenicity. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004;15:103–11 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 2
REFERENCES, SECTION 3
-
- Eigenmann PA. Future therapeutic options in food allergy. Allergy. 2003;58:1217–1223 - PubMed
-
- WHO, World Health Statistics 2009. Available at http://www.who.int/whosis/whostat/2009/en/print.html, accessed June 30, 2009.
-
- ISAAC Phase Three Study Group Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368:733–743 - PubMed
-
- Good Housekeeping Institute, Consumer Research Department. Childcare findings V, Children and Food. New York: A Good Housekeeping Report. 1989.
-
- Good Housekeeping Institute, Consumer Research Department. Women's opinions of food allergens. New York: A Good Housekeeping Institute Publication. 1984.
REFERENCES, SECTION 4
-
- Bahna SL. Cow's milk allergy versus cow milk intolerance. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002;89(Suppl 1):56–60 - PubMed
-
- Vesa TH, Marteau P, Korpela R. Lactose intolerance. J Am Coll Nutrit. 2000;19:165S–175S - PubMed
-
- Shukla H. Lactose Intolerance in health and disease. Nutr Food Sci. 1997;2:66–70
-
- Swallow DM, Hollox EJ. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001
-
- Cox TM. Food Allergy and Intolerance (chapt 25). London: Saunders; 2002
REFERENCES, SECTION 5
-
- Crittenden RG, Bennett LE. Cow's milk allergy: a complex disorder. J Am Coll Nutr. 2005;24(Suppl):582S–591S - PubMed
-
- van Wijk F, Knippels L. Initiating mechanisms of food allergy: Oral tolerance versus allergic sensitization. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007;61:8–20 - PubMed
-
- Majamaa H, Isolauri E. Evaluation of gut mucosal barrier: evidence for increased antigen transfer in children with atopic eczema. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;97:985–990 - PubMed
-
- Pike MG, Heddle RJ, Boulton P. Increased intestinal permeability in atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. 1986;86:101–104 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 6
-
- Sampson HA. Update on food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:805–819 - PubMed
-
- Allen KJ, Davidson GP, Day AS, Hill DJ, Kemp AS, et al. Management of cow's milk protein allergy in infants and young children: an expert panel perspective. J Paediatr Child Health. 2009;45:481–486 - PubMed
-
- Laiho K, Ouwehand A, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Inventing probiotic functional foods for patients with allergic disease. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002;89(6 Suppl 1):75–82 - PubMed
-
- Kawano Y, Nishida T, Yamagishi R, Noma T. A case of milk allergy that presented anaphylaxis after cutaneous contact with allergen. Allergology International. 2001;50:105–107
-
- Codreanu F, Morisset M, Cordebar V, Kanny G, Moneret-Vautren DA. Risk of allergy to food protein in topical medicinal agents and cosmetics. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;38:126–130 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 7
-
- Bahna SL. Diagnosis of food allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003;90:S77–S80 - PubMed
-
- Sampson HA. Food allergy. Part 2: diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:981–989 - PubMed
-
- Bock SA. Diagnostic evaluation. Pediatrics. 2003;111:1638–1644 - PubMed
-
- Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Assa'ad AH, Bahna SL, Bock SA, Sicherer SH, Teuber SS: Adverse Reactions to Food Committee of American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Work Group report: oral food challenge testing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123(Suppl):S365–S383 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 8
-
- Nowak-Wegrzyn A. Food allergy to proteins. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2007;59:17–31 - PubMed
-
- Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Fiocchi A. Rare, medium, or well done? The effect of heating and food matrix on food protein allergenicity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;9:234–237 - PubMed
-
- Fiocchi A, Restani P, Riva E. Beef allergy in children. Nutrition. 2000;16:454–457 - PubMed
-
- Werfel SJ, Cooke SK, Sampson HA. Clinical reactivity to beef in children allergic to cow's milk. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99:293–300 - PubMed
-
- Bahna SL. Food challenge procedures in research and in clinical practice. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1995;6(Suppl 8):49–53 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 9
-
- Baehler P, Chad Z, Gurbindo C, Bonin AP, Bouthillier L, Seidman EG. Distinct patterns of cow's milk allergy in infancy defined by prolonged, two-stage double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996;26:254–261 - PubMed
-
- Berni Canani R, Ruotolo S, Auricchio L, Caldore M, Porcaro F, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the atopy patch test in children with food allergy-related gastrointestinal symptoms. Allergy. 2007;62:738–743 - PubMed
-
- Calvani M, Alessandri C, Frediani T, Lucarelli S, Miceli SS, et al. Correlation between skin prick test using commercial extract of cow's milk protein and fresh milk and food challenge. Pediat Allergy Immunol. 2007;18:583–588 - PubMed
-
- Cudowska B, Kaczmarski M. Atopy patch test in the diagnosis of food allergy in children with atopic eczema dermatitis syndrome. Roczniki Akademii Medycznej W Bialymstoku. 2005;50:261–267 - PubMed
-
- Davidson GP, Hill DJ, Townley RR. Gastrointestinal milk allergy in childhood: a rational approach. Med J Aust. 1976;1:945–947 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 10
-
- Fiocchi A, Bouygue GR, Restani P, Bonvini G, Startari R, Terracciano L. Accuracy of skin prick tests in bovine protein allergy (BPA). Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2002;89:26–32 - PubMed
-
- Sicherer SH, Leung DY. Advances in allergic skin disease, anaphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reactions to foods, drugs, and insects in 2009. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:85–97 - PubMed
-
- Sicherer SH. Food allergy: when and how to perform oral food challenges. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1999;10:226–234 - PubMed
-
- Kaila M, Vanto T, Valovirta E, Koivikko A, Juntunen-Backman K. Diagnosis of food allergy in Finland: survey of pediatric practices. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2000;11:246–249 - PubMed
-
- Martelli A, Bouygue GR, Isoardi P, Marelli O, Sarratud T, Fiocchi A. Oral food challenges in children in Italy. Allergy. 2005;60:907–911 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 11
-
- The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. Lancet. 1998;351:1225–1232 - PubMed
-
- de Boissieu D, Matarazzo P, Rocchiccioli F, Dupont C. Multiple food allergy: a possible diagnosis in breastfed infants. Acta Pediatr. 1997;86:1042–1046 - PubMed
-
- Järvinen K-M, Mäkinen-Kiljunen S, Suomalainen H. Cow's milk challenge via human milk evokes immune responses in suckling infants with cow's milk allergy. J Pediatr. 1999;135:506–512 - PubMed
-
- Järvinen K-M, Suomalainen H. Development of cow's milk allergy in breast-fed infants. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 2001;31:978–987 - PubMed
-
- Miyazawa T, Itahashi K, Imai T. Management of neonatal cow's milk allergy in high-risk neonates. Pediatr Int. 2009;51:544–447 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 12
-
- American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology Food allergy: a practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;96(Suppl 2):S1–S68 - PubMed
-
- Fiocchi A, Bouygue GR, Martelli A, Terracciano L, Sarratud T. Dietary treatment of childhood atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome (AEDS). Allergy. 2004;59(Suppl 78):78–85 - PubMed
-
- Tan BM, Sher MR, Good RA, Bahna SL. Severe food allergies by skin contact. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86:583–586 - PubMed
-
- Roberts G, Lack G. Relevance of inhalational exposure to food allergens. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;3:211–215 - PubMed
-
- Fiocchi A, Bouygue GR, Restani P, Gaiaschi A, Terracciano L, Martelli A. Anaphylaxis to rice by inhalation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:193–195 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 13
-
- Isolauri E, Tahvanainen A, Peltola T. Breast-feeding of allergic infants. J Pediatr. 1999;134:27–32 - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Nutrition Hypoallergenic infant formulas. Pediatrics. 2000;106:346–349 - PubMed
-
- de Boissieu D, Dupont C. Allergy to extensively hydrolysed cows' milk proteins in infants: safety and duration of amino acid-based formula. J Pediatr. 2002;141:271–273 - PubMed
-
- Terracciano L, Isoardi P, Arrigoni S, Zoja A, Martelli A. Milk, soy and rice hydrolysates. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2002;89:86–90 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 14
-
- Hill DJ, Murch SH, Rafferty K, Wallis P, Green CJ. The efficacy of amino acid-based formulas in relieving the symptoms of cow's milk allergy: a systematic review. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:808–822 - PubMed
-
- Hill DJ, Cameron DJ, Francis DE, Gonzalez-Andaya AM, Hosking CS. Challenge confirmation of late-onset reactions to extensively hydrolyzed formulas in infants with multiple food protein intolerance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96:386–394 - PubMed
-
- Niggemann B, von BA, Bollrath C, Berdel D, Schauer U, et al. Safety and efficacy of a new extensively hydrolyzed formula for infants with cow's milk protein allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008;19:348–354 - PubMed
-
- Isolauri E, Sutas Y, Makinen-Kiljunen S, Oja SS, Isosomppi R, Turjanmaa K. Efficacy and safety of hydrolyzed cow milk and amino acid-derived formulas in infants with cow milk allergy. J Pediatr. 1995;127:550–557 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 15
-
- El-Agamy EI. The challenge of cow milk protein allergy. Small Ruminant Research. 2007;68:64–72
-
- El-Agamy EI, Nawar MA. Nutritive and immunological values of camel milk: a comparative study with milk of other species. In: Second International Camelid Conference: Agroeconomics of Camelid Farming, Almaty, Kazakhstan, 8–12 September 2000, 33–45.
-
- Spitzauer S. Allergy to mammalian proteins: at the borderline between foreign and self? Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999;120:259–269 - PubMed
-
- Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. ExPASy Proteomics Server, binary alignment (SIM + LANVIEW). Retrieved from http://www.expasy.org/ Accessed July 20, 2009.
-
- Restani P, Ballabio C, Di Lorenzo C, Tripodi S, Fiocchi A. Molecular aspects of milk allergens and their role in clinical events. Anal Bioanal Chem 2009. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 16
-
- Levy Y, Davidovits M. Nutritional rickets in children with cows' milk allergy: calcium deficiency or vitamin D deficiency? Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005;16:553. - PubMed
-
- Fox AT, Du Toit G, Lang A, Lack G. Food allergy as a risk factor for nutritional rickets. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004;15:566–569 - PubMed
-
- Agostoni C, Fiocchi A, Riva E, Terracciano L, Sarratud T, et al. Growth of infants with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy fed different formulae in the complementary feeding period. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007;18:599–606 - PubMed
-
- Isolauri E, Sutas Y, Salo MK, Isosomppi R, Kaila M. Elimination diet in cow's milk allergy: risk for impaired growth in young children. J Pediatr. 1998;132:1004–1009 - PubMed
REFERENCES, SECTION 18
-
- Longo G, Barbi E, Berti I, Meneghetti R, Pittalis A, Ronfani L, Ventura A. Specific oral tolerance induction in children with very severe cow's milk-induced reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:343–347 - PubMed
-
- Morisset M, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Guenard L, Cuny JM, Frentz P, et al. Oral desensitization in children with milk and egg allergies obtains recovery in a significant proportion of cases. A randomized study in 60 children with cow's milk allergy and 90 children with egg allergy. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;39:12–19 - PubMed
-
- Patriarca G, Buonomo A, Roncallo C, Del NM, Pollastrini E, et al. Oral desensitization in cow milk allergy: immunological findings. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2002;15:53–58 - PubMed
-
- Patriarca G, Nucera E, Pollastrini E, Roncallo C, De PT, et al. Oral specific desensitization in food-allergic children. Digestive Diseases Sci. 2007;52:1662–1672 - PubMed
REFERENCE, SECTION 19
-
- ISAAC Phase Three Study Group Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368:733–743 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

