Innovative DNA vaccine to break immune tolerance against tumor self-antigen
- PMID: 23268564
- PMCID: PMC3581028
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2012.141
Innovative DNA vaccine to break immune tolerance against tumor self-antigen
Abstract
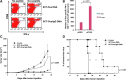
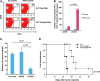
Vaccination is, in theory, a safe and effective approach for controlling disseminated or metastatic cancer due to the specificity of the mammalian immune system, yet its success in the clinic has been hampered thus far by the problem of immune tolerance to tumor self-antigen. Here we describe a DNA vaccination strategy that is able to control cancer by overcoming immune tolerance to tumor self-antigen. We engineered a DNA construct encoding a dimeric form of a secreted single-chain trimer of major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chain, β2-microglobulin, and peptide antigen linked to immunoglobulin G (SCT-Ag/IgG). The chimeric protein was able to bind to antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells with nearly 100% efficiency and strongly induce their activation and proliferation. In addition, the chimeric protein was able to coat professional antigen-presenting cells through the F(c) receptor to activate antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells. Furthermore, intradermal vaccination with DNA-encoding SCT-Ag/IgG could generate significant numbers of cytotoxic effector T cells against tumor self-antigen and leads to successful therapeutic outcomes in a preclinical model of metastatic melanoma. Our data suggest that the DNA vaccine strategy described in the current study is able to break immune tolerance against endogenous antigen from melanoma and result in potent therapeutic antitumor effects. Such strategy may be used in other antigenic systems for the control of infections and/or cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Chen C.H. Wang T.L. Hung C.F. Yang Y., et al. Enhancement of DNA vaccine potency by linkage of antigen gene to an HSP70 gene. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1035–42. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J.J. Ulmer J.B. Shiver J.W. Liu M.A. DNA vaccines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:617–48. - PubMed
-
- Fang L. Wang K. Liu X., et al. A study on anti-tumor immunity induced by gene-modified melanoma B16 cells. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:1589–95. - PubMed
-
- Gurunathan S. Klinman D.M. Seder R.A. DNA vaccines: immunology, application, and optimization. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:927–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

