L5 spinal nerve injury caused by misplacement of outwardly-inserted S1 pedicle screws
- PMID: 23269529
- PMCID: PMC3641263
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-012-2634-z
L5 spinal nerve injury caused by misplacement of outwardly-inserted S1 pedicle screws
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate L5 nerve root injuries caused by outwardly misplaced S1 pedicle screws. Pedicle screws remain the criterion standard for fixation of L5-S1 to correct lumbosacral instability. When inserting S1 pedicle screws, it is possible to injure the L5 nerve root if screws are inserted outwardly and the tip of the screw perforates the anterior cortex of the sacrum. Despite this risk, to our knowledge this type of injury has never been reported as a case series.
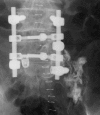
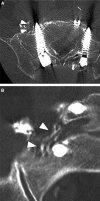
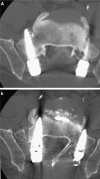
Methods: We experienced 2 cases of L5 nerve root injury caused by outwardly-inserted S1 pedicle screws. In both cases, bilateral S1 pedicle screws were inserted outwardly using a free-hand technique, and on one side, screws induced severe pain by impinging on an L5 root. Computed tomography after the selective rootgraphy of the injured nerve showed the nerve compressed laterally by screw threads in Case 1 and crushed between the screw threads and the sacral body in Case 2.
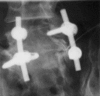
Results: In both cases, leg pain disappeared immediately after the infiltration of the nerve with lidocaine, but symptoms recurred within a few days in Case 1 and within an hour in Case 2. Conservative treatment of three spinal nerve infiltrations was effective in Case 1, but reinsertion of the rogue screw was necessary in Case 2.
Conclusions: Surgeons should recognize that lateral inclination of S1 pedicle screws can cause L5 nerve root injury, which may require reinsertion of the screw, especially in cases where insertion is difficult because of overlapping surrounding muscle or bony tissue.
Figures
References
-
- Ledonio CG, Polly DW, Jr, Vitale MG, Wang Q, Richards BS. Pediatric pedicle screws: comparative effectiveness and safety: a systematic literature review from the Scoliosis Research Society and the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America task force. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1227–1234. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00678. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

