VS-5584, a novel and highly selective PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer
- PMID: 23270925
- PMCID: PMC3588144
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0466
VS-5584, a novel and highly selective PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer
Abstract
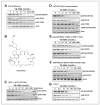
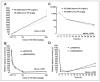
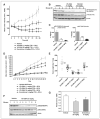
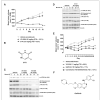
Dysregulation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway, either through amplifications, deletions, or as a direct result of mutations, has been closely linked to the development and progression of a wide range of cancers. Moreover, this pathway activation is a poor prognostic marker for many tumor types and confers resistance to various cancer therapies. Here, we describe VS-5584, a novel, low-molecular weight compound with equivalent potent activity against mTOR (IC(50) = 37 nmol/L) and all class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) isoforms IC(50): PI3Kα = 16 nmol/L; PI3Kβ = 68 nmol/L; PI3Kγ = 25 nmol/L; PI3Kδ = 42 nmol/L, without relevant activity on 400 lipid and protein kinases. VS-5584 shows robust modulation of cellular PI3K/mTOR pathways, inhibiting phosphorylation of substrates downstream of PI3K and mTORC1/2. A large human cancer cell line panel screen (436 lines) revealed broad antiproliferative sensitivity and that cells harboring mutations in PI3KCA are generally more sensitive toward VS-5584 treatment. VS-5584 exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic properties after oral dosing in mice and is well tolerated. VS-5584 induces long-lasting and dose-dependent inhibition of PI3K/mTOR signaling in tumor tissue, leading to tumor growth inhibition in various rapalog-sensitive and -resistant human xenograft models. Furthermore, VS-5584 is synergistic with an EGF receptor inhibitor in a gastric tumor model. The unique selectivity profile and favorable pharmacologic and pharmaceutical properties of VS-5584 and its efficacy in a wide range of human tumor models supports further investigations of VS-5584 in clinical trials.
©2012 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PF-04691502, a potent and selective oral inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR kinases with antitumor activity.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2189-99. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0185. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21750219
-
Antitumor efficacy of PKI-587, a highly potent dual PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 May 15;17(10):3193-203. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1694. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21325073
-
Preclinical characterization of OSI-027, a potent and selective inhibitor of mTORC1 and mTORC2: distinct from rapamycin.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Aug;10(8):1394-406. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1099. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21673091
-
Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Impact on Tumor Cells, Their Protective Stroma, Angiogenesis, and Immunotherapy.Cancer Discov. 2016 Oct;6(10):1090-1105. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0716. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27655435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Class (I) Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Mar 4;9(3):24. doi: 10.3390/cancers9030024. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28273837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The expression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer and its role in gastric cancer prognosis.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Sep 1;8:2427-33. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S88592. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26366097 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Strategies Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: An Updated Review.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2022 Jan 11;14:15-24. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S348060. eCollection 2022. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2022. PMID: 35046722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VS-5584, a Novel PI3K-mTOR Dual Inhibitor, Inhibits Melanoma Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 23;10(7):e0132655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132655. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26204252 Free PMC article.
-
Unique fractal evaluation and therapeutic implications of mitochondrial morphology in malignant mesothelioma.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 15;6:24578. doi: 10.1038/srep24578. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27080907 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of VS-5584 and Its Application in Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats.J Anal Methods Chem. 2020 Dec 16;2020:8811522. doi: 10.1155/2020/8811522. eCollection 2020. J Anal Methods Chem. 2020. PMID: 33381351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:329–41. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:550–62. - PubMed
-
- Huang S, Bjornsti MA, Houghton PJ. Rapamycins: mechanism of action and cellular resistance. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:222–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

