Why flavins are not competitors of chlorophyll in the evolution of biological converters of solar energy
- PMID: 23271372
- PMCID: PMC3565283
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14010575
Why flavins are not competitors of chlorophyll in the evolution of biological converters of solar energy
Abstract
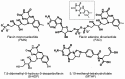
Excited flavin molecules can photocatalyze reactions, leading to the accumulation of free energy in the products, and the data accumulated through biochemical experiments and by modeling prebiological processes suggest that flavins were available in the earliest stages of evolution. Furthermore, model experiments have shown that abiogenic flavin conjugated with a polyamino acid matrix, a pigment that photocatalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP, could have been present in the prebiotic environment. Indeed, excited flavin molecules play key roles in many photoenzymes and regulatory photoreceptors, and the substantial structural differences between photoreceptor families indicate that evolution has repeatedly used flavins as chromophores for photoreceptor proteins. Some of these photoreceptors are equipped with a light-harvesting antenna, which transfers excitation energy to chemically reactive flavins in the reaction center. The sum of the available data suggests that evolution could have led to the formation of a flavin-based biological converter to convert light energy into energy in the form of ATP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Excited flavin and pterin coenzyme molecules in evolution.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2010 Oct;75(10):1200-16. doi: 10.1134/s0006297910100020. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2010. PMID: 21166638 Review.
-
Biological photoreceptors of light-dependent regulatory processes.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2013 Nov;78(11):1238-53. doi: 10.1134/S0006297913110047. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2013. PMID: 24460938 Review.
-
Catalysis by Nature's photoenzymes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Dec;77:102491. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102491. Epub 2022 Oct 30. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 36323132 Review.
-
A flavin binding cryptochrome photoreceptor responds to both blue and red light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant Cell. 2012 Jul;24(7):2992-3008. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098947. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22773746 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Flavins and Retbindin in Retinal Function and Homeostasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;854:643-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_85. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26427470
Cited by
-
Identification of a Novel Class of Photolyases as Possible Ancestors of Their Family.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Sep 27;38(10):4505-4519. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab191. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 34175934 Free PMC article.
-
Geochemistry and the Origin of Life: From Extraterrestrial Processes, Chemical Evolution on Earth, Fossilized Life's Records, to Natures of the Extant Life.Life (Basel). 2018 Sep 20;8(4):39. doi: 10.3390/life8040039. Life (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30241342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Molecular Structure of Pterins Suitable for Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 3;23(23):15222. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315222. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abiotic photophosphorylation model based on abiogenic flavin and pteridine pigments.J Mol Evol. 2013 May;76(5):332-42. doi: 10.1007/s00239-013-9562-3. Epub 2013 May 21. J Mol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23689512
References
-
- Whitmarsh J., Govindjee . The Photosynthetic Process. In: Singhal G.S., Renger G., editors. Concepts in Photobiology: Photosynthesis and Photomorphogenesis. Narosa Publishers; New Delhi, India: Kluwer Academic; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 1999. pp. 11–51.
-
- Osterhelt D. The structure and mechanism of the family of retinal proteins from halophilic Archaea. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1998;8:489–500. - PubMed
-
- Fischer M., Schott A.K., Romisch W., Ramsperger A., Augustin M., Fidler A., Bacher A., Richter G., Huber R., Eisenreich W. Evolution of vitamin B2 biosynthesis. A novel class of riboflavin synthase in Archaea. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;343:267–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

