Adaptive optics technology for high-resolution retinal imaging
- PMID: 23271600
- PMCID: PMC3574679
- DOI: 10.3390/s130100334
Adaptive optics technology for high-resolution retinal imaging
Abstract
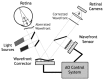
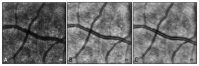
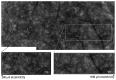
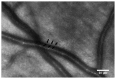
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effects of optical aberrations. The direct visualization of the photoreceptor cells, capillaries and nerve fiber bundles represents the major benefit of adding AO to retinal imaging. Adaptive optics is opening a new frontier for clinical research in ophthalmology, providing new information on the early pathological changes of the retinal microstructures in various retinal diseases. We have reviewed AO technology for retinal imaging, providing information on the core components of an AO retinal camera. The most commonly used wavefront sensing and correcting elements are discussed. Furthermore, we discuss current applications of AO imaging to a population of healthy adults and to the most frequent causes of blindness, including diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration and glaucoma. We conclude our work with a discussion on future clinical prospects for AO retinal imaging.
Figures




References
-
- Lombardo M., Lombardo G. Wave aberration of human eyes and new descriptors of image optical quality of the eye. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2010;36:313–331. - PubMed
-
- Thibos L.N., Hong X., Bradley A., Cheng X. Statistical variation of aberration structure and image quality in a normal population of healthy eyes. JOSA A. 2002;19:2329–2348. - PubMed
-
- Charman W.N., Chateau N. The prospects for super-acuity: Limits to visual performance after correction of monochromatic ocular aberration. Ophthalmic Physl. Opt. 2003;23:479–493. - PubMed
-
- Guirao A., Porter J., Williams D.R., Cox I.G. Calculated impact of higher-order monochromatic aberrations on retinal image quality in a population of human eyes. JOSA A. 2002;19:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

