Morbidity and mortality in heart transplant candidates supported with mechanical circulatory support: is reappraisal of the current United network for organ sharing thoracic organ allocation policy justified?
- PMID: 23271796
- PMCID: PMC3752367
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.100123
Morbidity and mortality in heart transplant candidates supported with mechanical circulatory support: is reappraisal of the current United network for organ sharing thoracic organ allocation policy justified?
Abstract
Background: Survival of patients on left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) has improved. We examined the differences in risk of adverse outcomes between LVAD-supported and medically managed candidates on the heart transplant waiting list.
Methods and results: We analyzed mortality and morbidity in 33,073 heart transplant candidates registered on the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) waiting list between 1999 and 2011. Five groups were selected: patients without LVADs in urgency status 1A, 1B, and 2; patients with pulsatile-flow LVADs; and patients with continuous-flow LVADs. Outcomes in patients requiring biventricular assist devices, total artificial heart, and temporary VADs were also analyzed. Two eras were defined on the basis of the approval date of the first continuous-flow LVAD for bridge to transplantation in the United States (2008). Mortality was lower in the current compared with the first era (2.1%/mo versus 2.9%/mo; P<0.0001). In the first era, mortality of pulsatile-flow LVAD patients was higher than in status 2 (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; P<0.0001) and similar to that in status 1B patients (HR, 1.04; P=0.61). In the current era, patients with continuous-flow LVADs had mortality similar to that of status 2 (HR, 0.80; P=0.12) and lower mortality compared with status 1A and 1B patients (HR, 0.24 and 0.47; P<0.0001 for both comparisons). However, status upgrade for LVAD-related complications occurred frequently (28%) and increased the mortality risk (HR, 1.75; P=0.001). Mortality was highest in patients with biventricular assist devices (HR, 5.00; P<0.0001) and temporary VADs (HR, 7.72; P<0.0001).
Conclusions: Mortality and morbidity on the heart transplant waiting list have decreased. Candidates supported with contemporary continuous-flow LVADs have favorable waiting list outcomes; however, they worsen significantly once a serious LVAD-related complication occurs. Transplant candidates requiring temporary and biventricular support have the highest risk of adverse outcomes. These results may help to guide optimal allocation of donor hearts.
Figures
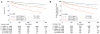
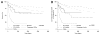
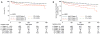
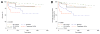
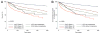
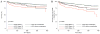
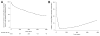

References
-
- Stehlik J, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Benden C, Christie JD, Dob-bels F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Hertz MI. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-eighth adult heart transplant report—2011. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011;30:1078–1094. - PubMed
-
- Renlund DG, Taylor DO, Kfoury AG, Shaddy RS. New UNOS rules: historical background and implications for transplantation management: United Network for Organ Sharing. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1999;18:1065–1070. - PubMed
-
- Zaroff JG, Rosengard BR, Armstrong WF, Babcock WD, D’Alessandro A, Dec GW, Edwards NM, Higgins RS, Jeevanandum V, Kauffman M, Kirklin JK, Large SR, Marelli D, Peterson TS, Ring WS, Robbins RC, Russell SD, Taylor DO, Van Bakel A, Wallwork J, Young JB. Consensus conference report: maximizing use of organs recovered from the cadaver donor: cardiac recommendations, March 28–29, 2001, Crystal City, Va. Circulation. 2002;106:836–841. - PubMed
-
- Chen JM, Sinha P, Rajasinghe HA, Suratwala SJ, McCue JD, McCarty MJ, Caliste X, Hauff HM, John R, Edwards NM. Do donor characteristics really matter? Short- and long-term impact of donor characteristics on recipient survival, 1995–1999. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2002;21:608–610. - PubMed
-
- Shafer TJ, Wagner D, Chessare J, Zampiello FA, McBride V, Perdue J. Organ donation breakthrough collaborative: increasing organ donation through system redesign. Crit Care Nurse. 2006;26:33–42. 44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

