Visual outcome after correcting the refractive error of large pupil patients with wavefront-guided ablation
- PMID: 23271878
- PMCID: PMC3526903
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S38182
Visual outcome after correcting the refractive error of large pupil patients with wavefront-guided ablation
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the efficacy and predictability of wavefront-guided laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) treatments using the iris registration (IR) technology for the correction of refractive errors in patients with large pupils.
Setting: Horus Vision Correction Center, Alexandria, Egypt.
Methods: Prospective noncomparative study including a total of 52 eyes of 30 consecutive laser refractive correction candidates with large mesopic pupil diameters and myopia or myopic astigmatism. Wavefront-guided LASIK was performed in all cases using the VISX STAR S4 IR excimer laser platform. Visual, refractive, aberrometric and mesopic contrast sensitivity (CS) outcomes were evaluated during a 6-month follow-up.
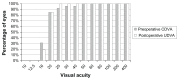
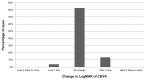
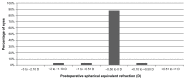
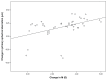
Results: Mean mesopic pupil diameter ranged from 8.0 mm to 9.4 mm. A significant improvement in uncorrected distance visual acuity (UCDVA) (P < 0.01) was found postoperatively, which was consistent with a significant refractive correction (P < 0.01). No significant change was detected in corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) (P = 0.11). Efficacy index (the ratio of postoperative UCDVA to preoperative CDVA) and safety index (the ratio of postoperative CDVA to preoperative CDVA) were calculated. Mean efficacy and safety indices were 1.06 ± 0.33 and 1.05 ± 0.18, respectively, and 92.31% of eyes had a postoperative spherical equivalent within ±0.50 diopters (D). Manifest refractive spherical equivalent improved significantly (P < 0.05) from a preoperative level of -3.1 ± 1.6 D (range -6.6 to 0 D) to -0.1 ± 0.2 D (range -1.3 to 0.1 D) at 6 months postoperative. No significant changes were found in mesopic CS (P ≥ 0.08), except CS for three cycles/degree, which improved significantly (P = 0.02). Magnitudes of primary coma and trefoil did not change significantly (P ≥ 0.34), with a small but statistically significant increase in primary spherical aberration.
Conclusion: Wavefront-guided LASIK provides an effective correction of low to moderate myopia or myopic astigmatism in large pupil patients without deterioration of visual quality.
Keywords: LASIK; large pupil; wavefront.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Four-year visual, refractive, and contrast sensitivity outcomes after wavefront-guided myopic LASIK using an advanced excimer laser platform.J Refract Surg. 2013 Dec;29(12):816-22. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20131023-04. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Refract Surg. 2013. PMID: 24168789
-
Induced Higher-order aberrations after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK) Performed with Wavefront-Guided IntraLase Femtosecond Laser in moderate to high Astigmatism.BMC Ophthalmol. 2016 Mar 22;16:29. doi: 10.1186/s12886-016-0205-5. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27000109 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of visual acuity and higher-order aberrations after standard and wavefront-guided myopic femtosecond LASIK].Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2015 Jan;71(1):44-50. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 25959784 Czech.
-
Comparison of refractive outcomes and high-order aberrations after small incision lenticule extraction and wavefront-guided femtosecond-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis for correcting high myopia and myopic astigmatism.Int Ophthalmol. 2020 Dec;40(12):3481-3489. doi: 10.1007/s10792-020-01534-x. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Int Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32737727
-
Excimer laser 6(th) generation: state of the art and refractive surgical outcomes.Eye Vis (Lond). 2015 Mar 1;2:6. doi: 10.1186/s40662-015-0015-5. eCollection 2015. Eye Vis (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26605362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Four-year follow-up of corneal aberrations and visual functions of myopic patients after laser in situ keratomileusis.Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Nov-Dec;31(6):1453-6. doi: 10.12669/pjms.316.8338. Pak J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26870114 Free PMC article.
-
Visual, aberrometric, photic phenomena, and patient satisfaction after myopic wavefront-guided LASIK using a high-resolution aberrometer.Clin Ophthalmol. 2016 Dec 12;10:2489-2496. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S108002. eCollection 2016. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 28003739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugar A, Rapuano CJ, Culberston WW, et al. Laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and astigmatism: safety and efficacy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2002;109(1):175–187. - PubMed
-
- Pesudovs K. Wavefront aberration outcomes of LASIK for high myopia and high hyperopia. J Refract Surg. 2005;21(5):S508–S512. - PubMed
-
- Kohnen T, Mahmoud K, Bühren J. Comparison of corneal higher-order aberrations induced by myopic and hyperopic LASIK. Ophthalmology. 2005;112(10):1692. - PubMed
-
- McCormick GJ, Porter J, Cox IG, MacRae S. Higher-order aberrations in eyes with irregular corneas after laser refractive surgery. Ophthalmology. 2005;112(10):1699–1708. - PubMed
-
- Llorente L, Barbero S, Merayo J, Marcos S. Total and corneal optical aberrations induced by laser in situ keratomileusis for hyperopia. J Refract Surg. 2004;20(3):203–216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

