Hypoxia-induced aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is due to increased expression of VEGF, IL-6 and miR-21, which can be attenuated by CDF treatment
- PMID: 23272057
- PMCID: PMC3521759
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050165
Hypoxia-induced aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is due to increased expression of VEGF, IL-6 and miR-21, which can be attenuated by CDF treatment
Abstract
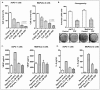
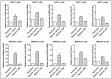
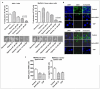
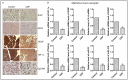
Hypoxia is known to play critical roles in cell survival, angiogenesis, tumor invasion, and metastasis. Hypoxia mediated over-expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) has been shown to be associated with therapeutic resistance, and contributes to poor prognosis of cancer patients. Emerging evidence suggest that hypoxia and HIF pathways contributes to the acquisition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), maintenance of cancer stem cell (CSC) functions, and also maintains the vicious cycle of inflammation-all which lead to therapeutic resistance. However, the precise molecular mechanism(s) by which hypoxia/HIF drives these events are not fully understood. Here, we show, for the first time, that hypoxia leads to increased expression of VEGF, IL-6, and CSC signature genes Nanog, Oct4 and EZH2 consistent with increased cell migration/invasion and angiogenesis, and the formation of pancreatospheres, concomitant with increased expression of miR-21 and miR-210 in human pancreatic cancer (PC) cells. The treatment of PC cells with CDF, a novel synthetic compound inhibited the production of VEGF and IL-6, and down-regulated the expression of Nanog, Oct4, EZH2 mRNAs, as well as miR-21 and miR-210 under hypoxia. CDF also led to decreased cell migration/invasion, angiogenesis, and formation of pancreatospheres under hypoxia. Moreover, CDF decreased gene expression of miR-21, miR-210, IL-6, HIF-1α, VEGF, and CSC signatures in vivo in a mouse orthotopic model of human PC. Collectively, these results suggest that the anti-tumor activity of CDF is in part mediated through deregulation of tumor hypoxic pathways, and thus CDF could become a novel, and effective anti-tumor agent for PC therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1): 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BK, Brown ML, Wingo PA, Howe HL, Ward E, et al. (2005) Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2002, featuring population-based trends in cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 97(19): 1407–1427. - PubMed
-
- Moulder JE, Rockwell S (1987) Tumor hypoxia: its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 5 4: 313–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

