Expression of BAFF and BAFF-R in follicular lymphoma: correlation with clinicopathologic characteristics and survival outcomes
- PMID: 23272079
- PMCID: PMC3521766
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050936
Expression of BAFF and BAFF-R in follicular lymphoma: correlation with clinicopathologic characteristics and survival outcomes
Abstract
Background: B-cell activation factor (BAFF) and BAFF-receptor (BAFF-R) play crucial roles in the viability and proliferation of malignant lymphoma cells. Limited information exists regarding expression profiles and the prognostic role of BAFF and BAFF-R in follicular lymphoma (FL). We sought to determine the expression profiles of BAFF and BAFF-R in FL and to evaluate the correlation of BAFF and BAFF-R expression with clinicopathologic characteristics and outcome of FL. Correlation between expression levels of BAFF detected by immunohistochemical (IHC) and serum levels of BAFF was also evaluated.
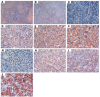
Methods: Paraffin-embedded specimens from 115 patients were immunohistochemically examined for BAFF and BAFF-R expression. Expression levels were dichotomized into low versus high categories based on immunostaining intensity. The correlation of BAFF and BAFF-R expression with clinicopathologic characteristics and patient outcome was assessed. Serum levels of BAFF in 35 of the 115 patients with IHC data were measured by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
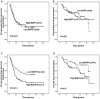
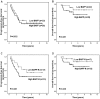
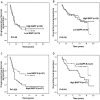
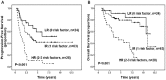
Results: BAFF and BAFF-R were expressed in 88.7% (102/115) and 87.8% (101/115) of the cases, respectively. BAFF expression was significantly correlated with only one clinicopathologic feature: Ann Arbor stage. No significant correlation was found between expression levels of BAFF detected by IHC and serum levels of BAFF detected by ELISA. High expression of BAFF-R, but not BAFF, was significantly correlated with inferior progression-free survival (PFS; P = 0.013) and overall survival (OS; P = 0.03). High expression of BAFF-R, bulky disease, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase were correlated with inferior PFS and OS in multivariate analysis. A prognostic scoring system incorporating these 3 risk factors identified 3 distinct prognostic groups with 5-year PFS of 59.4%, 41.9%, and 10.7% and OS of 91.3%, 79.7%, and 45.8%, respectively.
Conclusions: Most patients with FL variably express BAFF and BAFF-R. High expression of BAFF-R, but not BAFF, may be an independent risk factor for PFS and OS in FL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD (1998) New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol 16: 2780–2795. - PubMed
-
- Biagi JJ, Seymour JF (2002) Insights into the molecular pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma arising from analysis of geographic variation. Blood 99: 4265–4275. - PubMed
-
- Solal-Celigny P, Roy P, Colombat P, White J, Armitage JO, et al. (2004) Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index. Blood 104: 1258–1265. - PubMed
-
- Federico M, Bellei M, Marcheselli L, Luminari S, Lopez-Guillermo A, et al. (2009) Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index 2: a new prognostic index for follicular lymphoma developed by the international follicular lymphoma prognostic factor project. J Clin Oncol 27: 4555–4562. - PubMed
-
- Moore PA, Belvedere O, Orr A, Pieri K, LaFleur DW, et al. (1999) BLyS: member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 285: 260–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

