Evidence for small RNAs homologous to effector-encoding genes and transposable elements in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans
- PMID: 23272103
- PMCID: PMC3522703
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051399
Evidence for small RNAs homologous to effector-encoding genes and transposable elements in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans
Abstract
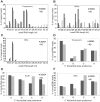
Phytophthora infestans is the oomycete pathogen responsible for the devastating late blight disease on potato and tomato. There is presently an intense research focus on the role(s) of effectors in promoting late blight disease development. However, little is known about how they are regulated, or how diversity in their expression may be generated among different isolates. Here we present data from investigation of RNA silencing processes, characterized by non-coding small RNA molecules (sRNA) of 19-40 nt. From deep sequencing of sRNAs we have identified sRNAs matching numerous RxLR and Crinkler (CRN) effector protein genes in two isolates differing in pathogenicity. Effector gene-derived sRNAs were present in both isolates, but exhibited marked differences in abundance, especially for CRN effectors. Small RNAs in P. infestans grouped into three clear size classes of 21, 25/26 and 32 nt. Small RNAs from all size classes mapped to RxLR effector genes, but notably 21 nt sRNAs were the predominant size class mapping to CRN effector genes. Some effector genes, such as PiAvr3a, to which sRNAs were found, also exhibited differences in transcript accumulation between the two isolates. The P. infestans genome is rich in transposable elements, and the majority of sRNAs of all size classes mapped to these sequences, predominantly to long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons. RNA silencing of Dicer and Argonaute genes provided evidence that generation of 21 nt sRNAs is Dicer-dependent, while accumulation of longer sRNAs was impacted by silencing of Argonaute genes. Additionally, we identified six microRNA (miRNA) candidates from our sequencing data, their precursor sequences from the genome sequence, and target mRNAs. These miRNA candidates have features characteristic of both plant and metazoan miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fragmentation of tRNA in Phytophthora infestans asexual life cycle stages and during host plant infection.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Dec 10;14:308. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0308-1. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25492044 Free PMC article.
-
Phytophthora infestans Argonaute 1 binds microRNA and small RNAs from effector genes and transposable elements.New Phytol. 2016 Aug;211(3):993-1007. doi: 10.1111/nph.13946. Epub 2016 Mar 24. New Phytol. 2016. PMID: 27010746
-
Silencing of the PiAvr3a effector-encoding gene from Phytophthora infestans by transcriptional fusion to a short interspersed element.Fungal Biol. 2011 Dec;115(12):1225-33. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2011.08.007. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Fungal Biol. 2011. PMID: 22115441
-
Phenotypic diversification by gene silencing in Phytophthora plant pathogens.Commun Integr Biol. 2013 Nov 1;6(6):e25890. doi: 10.4161/cib.25890. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Commun Integr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24563702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Does Phytophthora infestans Evade Control Efforts? Modern Insight Into the Late Blight Disease.Phytopathology. 2018 Aug;108(8):916-924. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-04-18-0130-IA. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Phytopathology. 2018. PMID: 29979126 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Functions of Small RNAs in Different Plant-Pathogen Communications.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 4;7:1552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01552. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27757103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogen small RNAs: a new class of effectors for pathogen attacks.Mol Plant Pathol. 2015 Apr;16(3):219-23. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12233. Mol Plant Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25764211 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Fragmentation of tRNA in Phytophthora infestans asexual life cycle stages and during host plant infection.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Dec 10;14:308. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0308-1. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25492044 Free PMC article.
-
Escaping Host Immunity: New Tricks for Plant Pathogens.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jul 7;12(7):e1005631. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005631. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27389195 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Prediction and validation of potential pathogenic microRNAs involved in Phytophthora infestans infection.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Mar;41(3):1879-89. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3037-5. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24430294
References
-
- Dick MW (2001) The Peronosporomycetes. In: McLaughlin DJ, McLaughlin EG, Lemke PA, eds. The Mycota. Vol VII. Systematics and evolution, Part A. Berlin Heidelberg New York, Springer. 39–72.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

